
What is correct about the monocot stem?
(A) Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous, vascular bundles are closed, phloem parenchyma is absent
(B) Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous, vascular bundles are open, phloem parenchyma is absent
(C) Hypodermis is collenchymatous, vascular bundles are closed, phloem parenchyma is present
(D) Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous, vascular bundles are closed, phloem parenchyma is present
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In monocot stems, the cambium is absent and xylem and phloem occur in direct contact with each other i.e there is no boundary present between them. There is no pith region in the monocot stem.
Complete answer:
Vascular bundles are closed in monocot stem. The sclerenchymatous hypodermis is present in a monocotyledonous stem. The hypodermis is two to three-layered thick and lies below the epidermis. It is made up of thick-walled lignified sclerenchyma fibers. Phloem parenchyma is absent in monocot stem.
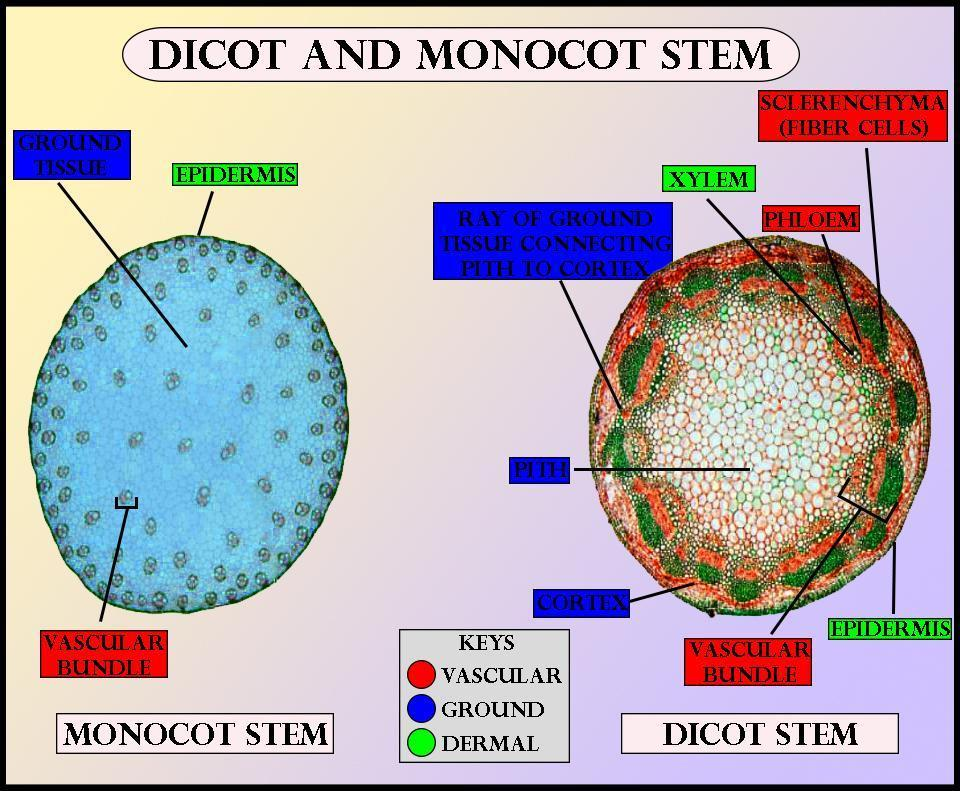
Epidermis: It is the outermost layer of the stem. It is made up of a single layer of tightly packed parenchymatous cells with a thick cuticle.
Hypodermis:
A few layers of sclerenchymatous cells which are lying below the epidermis constitute the hypodermis. Its function is to provide mechanical strength to the plant.
Ground tissue:
It is not differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith as it was in dicot stem.
The ground tissue is made up of several layers of loosely arranged parenchyma cells. The function of the ground tissue is the storage of food.
Vascular bundles:
Vascular bundles are not arranged in a ring in fact they are scattered in the parenchyma ground tissue.
Vascular bundles are numerous, small in size, and closely arranged in the peripheral portion.
Towards the center, the bundles are comparatively large in size and loosely arranged.
The vascular bundles are closed, conjoint, collateral, and endarch.
So, the correct answer is ‘(A) Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous, vascular bundles are closed, phloem parenchyma is absent’.
Note: Many of us get confused between xylem and phloem. Xylem is used to store and transport water and water-soluble nutrients to the plants. Phloem is used to transport organic nutrients. In xylem, the cell wall is made up of lignin and in the phloem, the cell wall is made up of cellulose.
Complete answer:
Vascular bundles are closed in monocot stem. The sclerenchymatous hypodermis is present in a monocotyledonous stem. The hypodermis is two to three-layered thick and lies below the epidermis. It is made up of thick-walled lignified sclerenchyma fibers. Phloem parenchyma is absent in monocot stem.

Epidermis: It is the outermost layer of the stem. It is made up of a single layer of tightly packed parenchymatous cells with a thick cuticle.
Hypodermis:
A few layers of sclerenchymatous cells which are lying below the epidermis constitute the hypodermis. Its function is to provide mechanical strength to the plant.
Ground tissue:
It is not differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith as it was in dicot stem.
The ground tissue is made up of several layers of loosely arranged parenchyma cells. The function of the ground tissue is the storage of food.
Vascular bundles:
Vascular bundles are not arranged in a ring in fact they are scattered in the parenchyma ground tissue.
Vascular bundles are numerous, small in size, and closely arranged in the peripheral portion.
Towards the center, the bundles are comparatively large in size and loosely arranged.
The vascular bundles are closed, conjoint, collateral, and endarch.
So, the correct answer is ‘(A) Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous, vascular bundles are closed, phloem parenchyma is absent’.
Note: Many of us get confused between xylem and phloem. Xylem is used to store and transport water and water-soluble nutrients to the plants. Phloem is used to transport organic nutrients. In xylem, the cell wall is made up of lignin and in the phloem, the cell wall is made up of cellulose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




