
Count the total number of $X-O$ bonds having equal length in $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ and ${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$ respectively. (If the answer is $5$ and $3$ then represent $53$).
A. $36$
B. $40$
C. $42$
D. $44$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Before talking about the answer, you should know about what bond length is. It is defined as the average distance between two bonded atoms in a molecule. By drawing the structures of the given ions we can figure out which bonds have equal length .
Complete step by step answer:
Now, in this question, in $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ , there are three equal bond lengths, which are present due to resonance.
$HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$
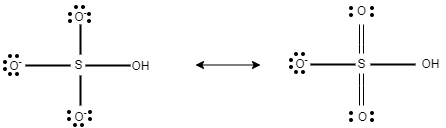
In $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ , the charge on each oxygen atom is $-1$ . Here, this $-1$ charge is evenly distributed on three oxygen atoms.
Now , In ${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$ , there are six equal bond lengths, which are present due to resonance.
${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$
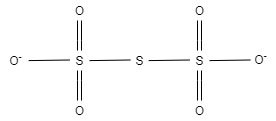
In ${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$ , the charge on each oxygen atom is $-1$ . Here, this $-1$ charge is evenly distributed on two oxygen atoms. Other four oxygen atoms are bonded with sulphur.
So, the correct answer is Option A ,$36$.
Note: 1.Bond length is defined as the average distance between the nucleus of two bonded atoms in a molecule. When there is a greater number of electrons that get participated in bond foundation, the bond length is shorter.
2.Resonance is defined as a combination of several contributing structures that describes bonding. This is known as resonance. It contains delocalized electrons where the whole bonding cannot be explained by one Lewis structure.
3.Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. Bond order is defined as the number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule. For example, $N\equiv N$ has bond order equals $3$ . To calculate bond order between two bonded atoms, then firstly, you have to draw the Lewis structure. After that, you should determine the types of bonds between the atoms in a molecule. It can be single bond, double bond or triple bond. If you get the bond order equal to zero, then the molecule cannot be formed. If the bond order is high, then the molecule is stable.
Note:
4.The formation of a resonating structure to calculate the number of bond lengths is necessary.
Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order.
\[Bond{ }\;length\propto \dfrac{1}{Bond\;{ order}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Now, in this question, in $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ , there are three equal bond lengths, which are present due to resonance.
$HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$

In $HS{{O}_{4}}^{-}$ , the charge on each oxygen atom is $-1$ . Here, this $-1$ charge is evenly distributed on three oxygen atoms.
Now , In ${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$ , there are six equal bond lengths, which are present due to resonance.
${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$

In ${{S}_{3}}{{O}_{6}}^{2-}$ , the charge on each oxygen atom is $-1$ . Here, this $-1$ charge is evenly distributed on two oxygen atoms. Other four oxygen atoms are bonded with sulphur.
So, the correct answer is Option A ,$36$.
Note: 1.Bond length is defined as the average distance between the nucleus of two bonded atoms in a molecule. When there is a greater number of electrons that get participated in bond foundation, the bond length is shorter.
2.Resonance is defined as a combination of several contributing structures that describes bonding. This is known as resonance. It contains delocalized electrons where the whole bonding cannot be explained by one Lewis structure.
3.Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. Bond order is defined as the number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule. For example, $N\equiv N$ has bond order equals $3$ . To calculate bond order between two bonded atoms, then firstly, you have to draw the Lewis structure. After that, you should determine the types of bonds between the atoms in a molecule. It can be single bond, double bond or triple bond. If you get the bond order equal to zero, then the molecule cannot be formed. If the bond order is high, then the molecule is stable.
Note:
4.The formation of a resonating structure to calculate the number of bond lengths is necessary.
Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order.
\[Bond{ }\;length\propto \dfrac{1}{Bond\;{ order}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




