
What is the countercurrent mechanism? Describe the physiological basis of the countercurrent mechanism in the kidney.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The process of transportation of various substances and particles in different directions to maintain a concentration gradient in the kidney resulting in the formation of the urine depending upon the concentration.
Complete answer:
The countercurrent mechanism is the process of creating a concentration gradient and forming concentrated urine. In this process, the energy is required to create a concentration gradient and move the substances in opposite directions. It is a characteristic feature of the mammalian kidneys. The process is involved in the formation of hypertonic urine. This mechanism is also found in the case of birds.
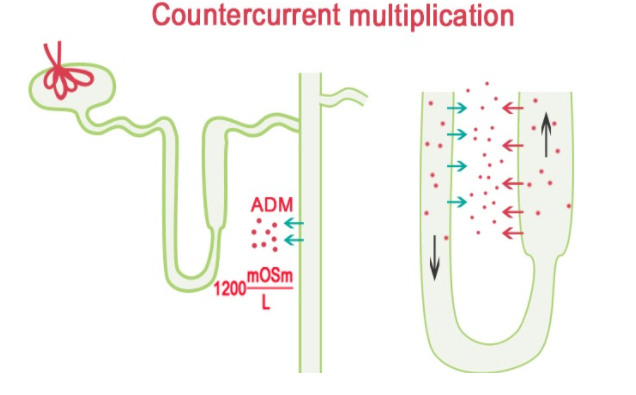
The urine is concentrated in the nephrons, which is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. The process occurs in the loop of Henle of the renal tubules present in the kidney. There are two renal tubules that run opposite to each other to create a countercurrent mechanism and in between both the tubules a renal medulla which is an interstitial space is present.
The two tubules of the renal medulla are the descending and the ascending loops. The descending loop of Henle consists of aquaporins which allow the transport of water but do not allow solutes to enter the tubular wall. This water then is transported to the medullary space and makes the urine hypertonic. The hypertonic urine is then transmitted to the ascending loop of Henle where the walls are permeable to ions but impermeable to water making the urine hypotonic. This process is known as the countercurrent mechanism of the kidney.
Note: The countercurrent mechanism is based on the postulates of Werner Kuhn. The mechanism was studied by Gottschalk and Mylle in 1950. This mechanism occurs in the juxtamedullary nephrons. The juxtamedullary nephrons have embedded proximal convoluted tubules inside the loop of Henle and its renal corpuscle is present near the medulla.
Complete answer:
The countercurrent mechanism is the process of creating a concentration gradient and forming concentrated urine. In this process, the energy is required to create a concentration gradient and move the substances in opposite directions. It is a characteristic feature of the mammalian kidneys. The process is involved in the formation of hypertonic urine. This mechanism is also found in the case of birds.
The urine is concentrated in the nephrons, which is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. The process occurs in the loop of Henle of the renal tubules present in the kidney. There are two renal tubules that run opposite to each other to create a countercurrent mechanism and in between both the tubules a renal medulla which is an interstitial space is present.
The two tubules of the renal medulla are the descending and the ascending loops. The descending loop of Henle consists of aquaporins which allow the transport of water but do not allow solutes to enter the tubular wall. This water then is transported to the medullary space and makes the urine hypertonic. The hypertonic urine is then transmitted to the ascending loop of Henle where the walls are permeable to ions but impermeable to water making the urine hypotonic. This process is known as the countercurrent mechanism of the kidney.

Note: The countercurrent mechanism is based on the postulates of Werner Kuhn. The mechanism was studied by Gottschalk and Mylle in 1950. This mechanism occurs in the juxtamedullary nephrons. The juxtamedullary nephrons have embedded proximal convoluted tubules inside the loop of Henle and its renal corpuscle is present near the medulla.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




