
Create a food chain depicting four trophic levels. Why do we not find the food chain more than four trophic levels in nature?
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Energy trapped by organisms does not remain in it forever. There is a process of energy transfer from one organism to another. The energy trapped by one organism is transferred into another is called a food chain. Organisms occupy a specific position in the food chain that are known as their trophic level.
Complete step by step answer:
i. Producers: Green plants, algae and some bacteria that make their own food are called producers.
ii. Consumer: These are animals that consume other animals or plants. Example: lion, tiger, eagle, snake, cow, goat. Consumers are divided into the following:
a. Primary consumers: Organisms that eat green plants/producers are called herbivores or primary consumers. Example goat, deer, cow, etc. It includes all herbivores animals.
b. Secondary consumers: Organisms that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers.
c. Tertiary consumer: Organisms that eat secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers.
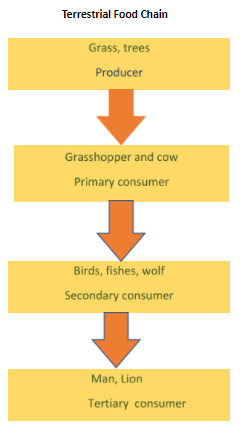
10 percent law: Only ten per cent of the energy is transferred from one organism to another. In more than the fourth trophic level of the food chain, there is very less energy or no energy to transfer. Hence, only three or four trophic levels in the food chain are possible.
Additional information: Food Web: Number of the connected food chains with each other make a web-like pattern called a food web. Instead of straight-line like in the food chain, the food web consists of branching lines.
Note: Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) are the solar radiation that plant traps to make food by the photosynthetic process. Only two to ten per cent photosynthetically active radiation is absorbed by plants and the whole living world depends on this small amount of life.
Complete step by step answer:
i. Producers: Green plants, algae and some bacteria that make their own food are called producers.
ii. Consumer: These are animals that consume other animals or plants. Example: lion, tiger, eagle, snake, cow, goat. Consumers are divided into the following:
a. Primary consumers: Organisms that eat green plants/producers are called herbivores or primary consumers. Example goat, deer, cow, etc. It includes all herbivores animals.
b. Secondary consumers: Organisms that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers.
c. Tertiary consumer: Organisms that eat secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers.

10 percent law: Only ten per cent of the energy is transferred from one organism to another. In more than the fourth trophic level of the food chain, there is very less energy or no energy to transfer. Hence, only three or four trophic levels in the food chain are possible.
Additional information: Food Web: Number of the connected food chains with each other make a web-like pattern called a food web. Instead of straight-line like in the food chain, the food web consists of branching lines.
Note: Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) are the solar radiation that plant traps to make food by the photosynthetic process. Only two to ten per cent photosynthetically active radiation is absorbed by plants and the whole living world depends on this small amount of life.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




