
What is the critical angle? Explain it with neat ray diagram
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Critical angle is related to refraction. It is also known as the largest angle of incidence for refraction.
Beyond the critical angle total internal reflection occurs.
Complete step by step answer:
When a certain critical value is reached by the angle of incidence in water, the refracted ray lies along the boundary, having a ninety degree refraction angle. This incidence angle is referred to as the critical angle.
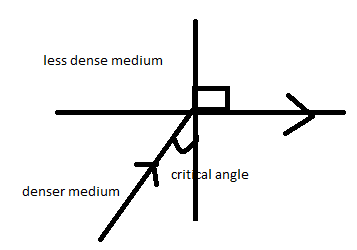
To know the critical angle we have to know what is refractive index and total internal reflection-
The refractive index also referred to as the index of refraction measures the bending of a ray of light as it moves from one medium to another.
When a ray of light in a passes through different mediums it totally reflects the light back into the same medium from which it came. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection.
The real value of the critical angle depends entirely on the combination of materials on each side of the boundary that are available.
Now let us consider two mediums. Let ${n_i}$ be the refractive index of the less dense medium or the incident medium.
Let ${n_r}$ be the refractive index of the denser medium or the refractive medium.
Let ${\theta _c}$be the critical angle of the medium.
Here ${\theta _c} = {\theta _i}$
Now we can find the critical angle with the help of the snell’s law-
Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of a wave’s angles of incidence and refraction is constant when it passes between two media.
So, mathematically-
$ {n_i}\sin {\theta _i} = {n_r}\sin {\theta _r} \\\implies {n_i}\sin {\theta _c} = {n_r}\sin 90 \\\implies{n_i}\sin {\theta _c} = {n_r} \\\implies\sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{{{n_r}}}{{{n_i}}} \\ \\ $
This is the required expression for the critical angle.
Note:
While calculating the critical angle we have to always keep in mind the medium from which the incident ray is coming. The medium of incidence should always be less dense than the medium of refraction.
Beyond the critical angle total internal reflection occurs.
Complete step by step answer:
When a certain critical value is reached by the angle of incidence in water, the refracted ray lies along the boundary, having a ninety degree refraction angle. This incidence angle is referred to as the critical angle.

To know the critical angle we have to know what is refractive index and total internal reflection-
The refractive index also referred to as the index of refraction measures the bending of a ray of light as it moves from one medium to another.
When a ray of light in a passes through different mediums it totally reflects the light back into the same medium from which it came. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection.
The real value of the critical angle depends entirely on the combination of materials on each side of the boundary that are available.
Now let us consider two mediums. Let ${n_i}$ be the refractive index of the less dense medium or the incident medium.
Let ${n_r}$ be the refractive index of the denser medium or the refractive medium.
Let ${\theta _c}$be the critical angle of the medium.
Here ${\theta _c} = {\theta _i}$
Now we can find the critical angle with the help of the snell’s law-
Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of a wave’s angles of incidence and refraction is constant when it passes between two media.
So, mathematically-
$ {n_i}\sin {\theta _i} = {n_r}\sin {\theta _r} \\\implies {n_i}\sin {\theta _c} = {n_r}\sin 90 \\\implies{n_i}\sin {\theta _c} = {n_r} \\\implies\sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{{{n_r}}}{{{n_i}}} \\ \\ $
This is the required expression for the critical angle.
Note:
While calculating the critical angle we have to always keep in mind the medium from which the incident ray is coming. The medium of incidence should always be less dense than the medium of refraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




