
What is crossing over? Write the significance of crossing over.
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: Crossing over leads to variations. It is an important step that occurs during meiotic cell division in prophase. It results in the exchange of genetic material. Crossing over takes place between two non-sister chromatids. Recombination is the product of crossing over.
Complete answer:Meiosis is a special kind of cell division that occurs generally in gamete cells. It is a reduction division that makes haploid gametes. This means that the resulting daughter cells have half the number of the normal set of chromosomes. These haploid chromosomes from two different parents fuse to form a zygote that restores a normal set of chromosomes. The resulting zygote shows variations in its phenotypic characters. This is due to crossing over.
Now, crossing over is an important step that occurs during the pachytene stage of meiosis, specifically during the prophase. It involves a pair of homologous chromosomes. At this stage, the chromosomes consist of four chromatids. The chromatids belonging to one chromosome are sister chromatids. Chromatids situated individually on a different chromosome that is one of the homologous chromosomes are called non-sister chromatids. The crossing takes place between these non-sister chromatid strands. During crossing over exchange of genetic material from one chromatid to another chromatid takes place. This results in a change in the genetic make-up of resulting gametes. This makes gametes different from the parent carrying them. This is also called the recombination of genetic material. Thus when gametes from two different parents fuse they add further variations due to a mixture of two types of genetic makeup.
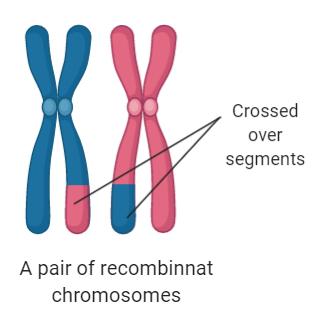
Significance of crossing over:
As it occurs in sexually reproducing organisms it ensures variations in offsprings attributing to their specific identities.
Sometimes the recombinations turn out to be beneficial due to superior characters. Thus, crossing over is extensively used by plant breeders to enhance crop varieties.
Crossing over leads to recombination that further produces a new combination of genes.
Note:Crossing over leads to the separation of linked genes. The frequency of crossing over varies from 0-50 percent but can exceed 50 percent. Crossing over also provides an equal frequency of parental and recombinant types to appear in a test cross.
Complete answer:Meiosis is a special kind of cell division that occurs generally in gamete cells. It is a reduction division that makes haploid gametes. This means that the resulting daughter cells have half the number of the normal set of chromosomes. These haploid chromosomes from two different parents fuse to form a zygote that restores a normal set of chromosomes. The resulting zygote shows variations in its phenotypic characters. This is due to crossing over.
Now, crossing over is an important step that occurs during the pachytene stage of meiosis, specifically during the prophase. It involves a pair of homologous chromosomes. At this stage, the chromosomes consist of four chromatids. The chromatids belonging to one chromosome are sister chromatids. Chromatids situated individually on a different chromosome that is one of the homologous chromosomes are called non-sister chromatids. The crossing takes place between these non-sister chromatid strands. During crossing over exchange of genetic material from one chromatid to another chromatid takes place. This results in a change in the genetic make-up of resulting gametes. This makes gametes different from the parent carrying them. This is also called the recombination of genetic material. Thus when gametes from two different parents fuse they add further variations due to a mixture of two types of genetic makeup.

Significance of crossing over:
As it occurs in sexually reproducing organisms it ensures variations in offsprings attributing to their specific identities.
Sometimes the recombinations turn out to be beneficial due to superior characters. Thus, crossing over is extensively used by plant breeders to enhance crop varieties.
Crossing over leads to recombination that further produces a new combination of genes.
Note:Crossing over leads to the separation of linked genes. The frequency of crossing over varies from 0-50 percent but can exceed 50 percent. Crossing over also provides an equal frequency of parental and recombinant types to appear in a test cross.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




