
Cross-pollination is favoured by
(a) Self-sterility
(b) Dichogamy
(c) Herkogamy and heterostyly
(d) All of these
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Cross-pollination is when a plant of another type is pollinated by one plant. A common technique used by hermaphroditic angiosperms to minimize sexual interference is one characteristic. Self incompatibility is another trait.
Complete answer:
The genetic material of the two plants is mixed in cross-pollination and the resulting seeds from that pollination would have characteristics of both varieties and are a new variety.
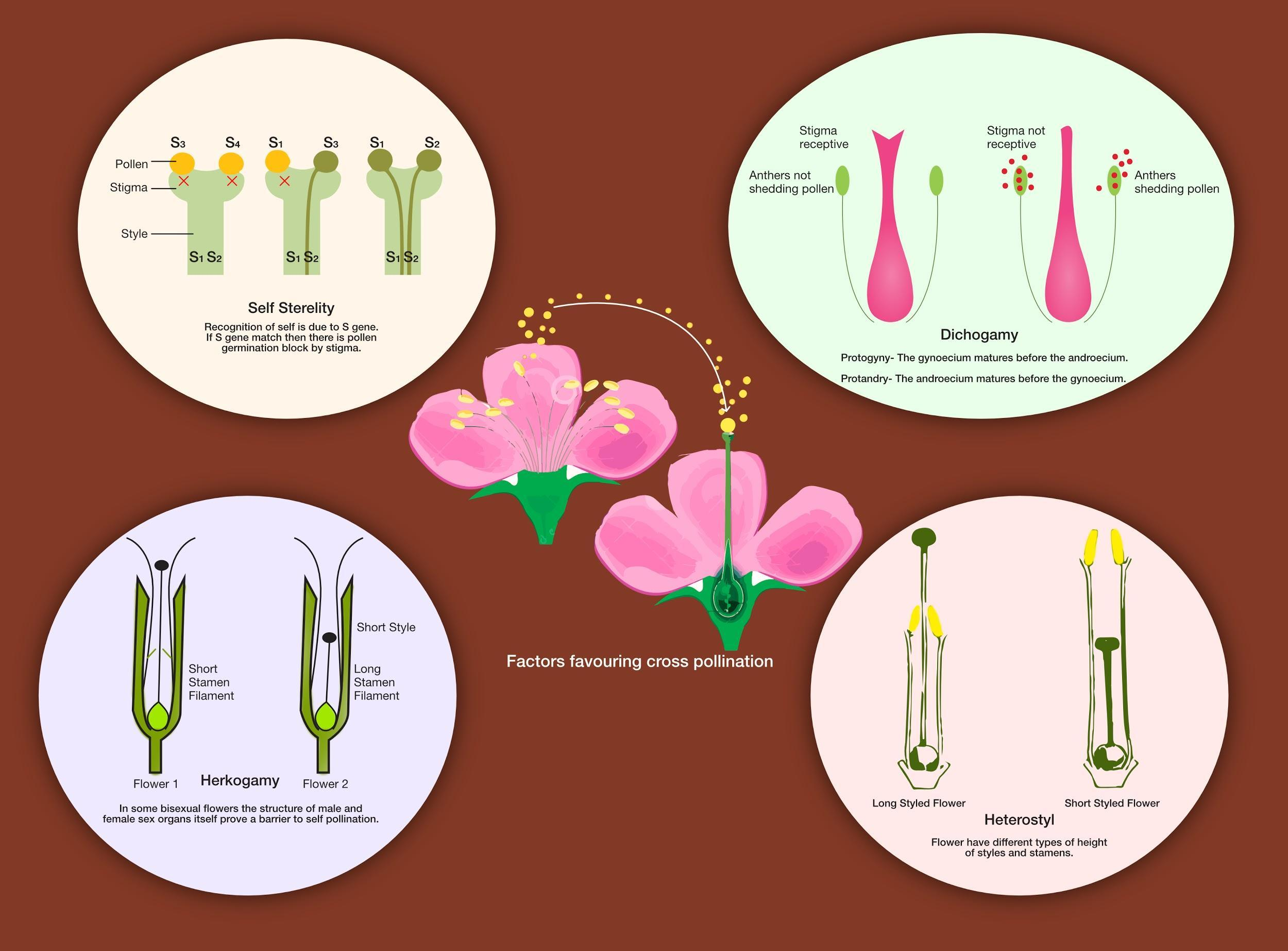
By cross-pollination, many numbers of species are pollinated. Unisexuality, dichogamy, self-sterility, mechanical and structural barrier, and heterostyle are the variables favoring cross-pollination.
- To avoid self-fertilization and improve family diversification, self-sterility in plants is enhanced.
- Dichogamy is the ripening of a flower's stamens and pistils at various times in order to avoid self-fertilization.
- Herkogamy is a common technique used by hermaphroditic angiosperms to minimize the role of male (anthers) and female (stigma) sexual interference.
- Heterostyly in flowers is a rare type of polymorphism and herkogamy. Two or three morphological forms of flowers in a heterostyle species occur in the population. All these avoid and favour cross-pollination from self-pollination.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) All of these’.
Note: Cross-pollination is the movement of pollen from one flower's anther to another flower's stigma to another of the same species' separate individuals.
Self-sterility or self-incompatibility is the phenomenon in which a plant is unable to conduct successful self-fertilization, i.e. by inhibiting pollen germination or the growth of pollen tubes on the pistil, prevents self-pollen from fertilizing the ovules. As fertilization does not occur, there is no creation of seeds.
Complete answer:
The genetic material of the two plants is mixed in cross-pollination and the resulting seeds from that pollination would have characteristics of both varieties and are a new variety.

By cross-pollination, many numbers of species are pollinated. Unisexuality, dichogamy, self-sterility, mechanical and structural barrier, and heterostyle are the variables favoring cross-pollination.
- To avoid self-fertilization and improve family diversification, self-sterility in plants is enhanced.
- Dichogamy is the ripening of a flower's stamens and pistils at various times in order to avoid self-fertilization.
- Herkogamy is a common technique used by hermaphroditic angiosperms to minimize the role of male (anthers) and female (stigma) sexual interference.
- Heterostyly in flowers is a rare type of polymorphism and herkogamy. Two or three morphological forms of flowers in a heterostyle species occur in the population. All these avoid and favour cross-pollination from self-pollination.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) All of these’.
Note: Cross-pollination is the movement of pollen from one flower's anther to another flower's stigma to another of the same species' separate individuals.
Self-sterility or self-incompatibility is the phenomenon in which a plant is unable to conduct successful self-fertilization, i.e. by inhibiting pollen germination or the growth of pollen tubes on the pistil, prevents self-pollen from fertilizing the ovules. As fertilization does not occur, there is no creation of seeds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




