
What is d.c. motor? Explain its construction and working with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint : The DC motor converts direct current electricity into mechanical energy. The magnetic field exerts a force on the armature as the current flows through the coil.
Complete step by step answer
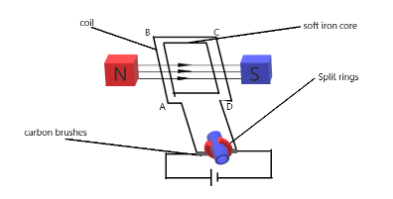
A dc motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
A dc motor is constructed by placing a rectangular coil of wire, called the armature, in a magnetic field. Usually a shaft is attached to the armature to allow transmission of mechanical energy. The major parts of a dc motor are the permanent magnets or electromagnet, to create a magnetic field, the armature (coil and soft iron core), the commutator, consisting of split rings and brushes.
When a current starts to flow from the cell into the armature, through A, the force on the left part of the coil (AB) will be directed downward as given by Fleming's left hand rule, while the right part (CD) will be directed upward. This creates a net torque which causes rotation about the centre of the armature. When the armature rotates 90 degrees, the split rings (which are permitted to move) lose contact with the brushes, and hence zero current flows but the armature will continue to rotate as a result of its angular momentum. As it goes beyond 90 degrees towards the 180 degree, the split ring which was on the right is now on the left, hence, the current still flows through the armature in the same direction.
This allows the motor to continually turn as long as electricity still runs through the armature.
Hence the electrical energy has been converted to mechanical energy.
Note
For clarity, we should note that if the brushes move with the rings, towards the 180 degree turn, the current in the armature would have been reversed since the side AB would now be at the side CB still carrying current upward. This means that the current will flow anti-clockwise (in contrast to the clockwise motion initially). This allows the direction of the torque to be reversed, hence causing an oscillation of the armature rather than a complete 360 degree rotation.
Complete step by step answer

A dc motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
A dc motor is constructed by placing a rectangular coil of wire, called the armature, in a magnetic field. Usually a shaft is attached to the armature to allow transmission of mechanical energy. The major parts of a dc motor are the permanent magnets or electromagnet, to create a magnetic field, the armature (coil and soft iron core), the commutator, consisting of split rings and brushes.
When a current starts to flow from the cell into the armature, through A, the force on the left part of the coil (AB) will be directed downward as given by Fleming's left hand rule, while the right part (CD) will be directed upward. This creates a net torque which causes rotation about the centre of the armature. When the armature rotates 90 degrees, the split rings (which are permitted to move) lose contact with the brushes, and hence zero current flows but the armature will continue to rotate as a result of its angular momentum. As it goes beyond 90 degrees towards the 180 degree, the split ring which was on the right is now on the left, hence, the current still flows through the armature in the same direction.
This allows the motor to continually turn as long as electricity still runs through the armature.
Hence the electrical energy has been converted to mechanical energy.
Note
For clarity, we should note that if the brushes move with the rings, towards the 180 degree turn, the current in the armature would have been reversed since the side AB would now be at the side CB still carrying current upward. This means that the current will flow anti-clockwise (in contrast to the clockwise motion initially). This allows the direction of the torque to be reversed, hence causing an oscillation of the armature rather than a complete 360 degree rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




