
Define a coordinate bond and give the conditions for its formation. Explain with an example.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: One of the atoms that is involved in bonding should be electron deficient.
Lone pair is a prerequisite for bond formation.
Complete Solution :
A coordinate bond is a bond formed between two atoms in which the electrons shared between the two atoms, for the bond formation completely belongs to one atom, i.e. one atom alone contributes its two electrons for the bond formation. Such a type of bond formed is called the co-ordinate bond. And it is represented by an arrow mark from the atom which had shared its electrons to the atom to which the electrons have been donated.
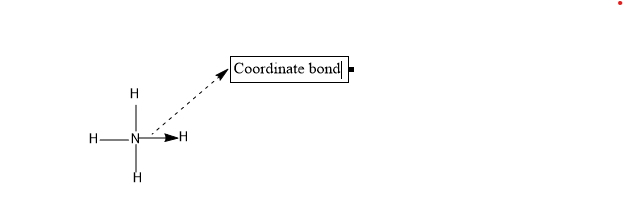
Coordinate bond is also called a dative bond or a dipolar bond.
- The conditions for the formation of coordinate bond is-
-One of the atoms involved should be electron rich and must possess a lone pair, which is ready to share with the other atom during the formation of coordinate bonds. Such atoms are called the donor atom since it is the atom which is donating the electron.
-The acceptor atom which is accepting the electrons from the donor atom should be electron deficient. The Acceptor atom is also called the receptor atom.
Example-One of the examples, where we can see a coordinate bond is the formation of $N{{H}_{_{4}}}^{+}$.
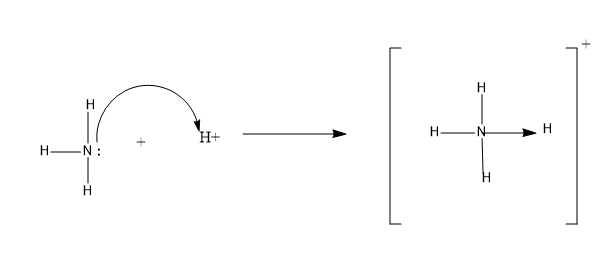
(Ammonium ion)
The N atom in the ammonia donates a pair of electrons to the ${{H}^{+}}$ to form the ammonium ion. Here N atom is the donor atom and ${{H}^{+}}$ is an acceptor atom.
Note: The coordinate bond is a directional bond, i.e. the sharing of electrons will take place in one direction.
- The co-ordinate bond is weaker than ionic bonding, and the way to find coordination bonds whether present or not in a compound is through drawing the Lewis dot structure and checking if there is any possibility for the atom to form covalent bonds, if covalent bonds can’t be formed then it will form coordinate bonds.
Lone pair is a prerequisite for bond formation.
Complete Solution :
A coordinate bond is a bond formed between two atoms in which the electrons shared between the two atoms, for the bond formation completely belongs to one atom, i.e. one atom alone contributes its two electrons for the bond formation. Such a type of bond formed is called the co-ordinate bond. And it is represented by an arrow mark from the atom which had shared its electrons to the atom to which the electrons have been donated.

Coordinate bond is also called a dative bond or a dipolar bond.
- The conditions for the formation of coordinate bond is-
-One of the atoms involved should be electron rich and must possess a lone pair, which is ready to share with the other atom during the formation of coordinate bonds. Such atoms are called the donor atom since it is the atom which is donating the electron.
-The acceptor atom which is accepting the electrons from the donor atom should be electron deficient. The Acceptor atom is also called the receptor atom.
Example-One of the examples, where we can see a coordinate bond is the formation of $N{{H}_{_{4}}}^{+}$.

(Ammonium ion)
The N atom in the ammonia donates a pair of electrons to the ${{H}^{+}}$ to form the ammonium ion. Here N atom is the donor atom and ${{H}^{+}}$ is an acceptor atom.
Note: The coordinate bond is a directional bond, i.e. the sharing of electrons will take place in one direction.
- The co-ordinate bond is weaker than ionic bonding, and the way to find coordination bonds whether present or not in a compound is through drawing the Lewis dot structure and checking if there is any possibility for the atom to form covalent bonds, if covalent bonds can’t be formed then it will form coordinate bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




