
Define Alternating current and explain the working of the device which produces it. Draw labeled diagram.Describe the change in direction of current
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: AC voltages are produced across the wire in accordance with Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction.
Complete step by step answer:
Definition of Alternating current:-
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses its direction, and changes its magnitude continuously with time. However, in direct current (DC), it flows only in one direction.
AC Generator:-
AC generators are the device that produces alternating current. In the AC generators, an armature rotates between the poles of the magnet (which provide magnetic field) on an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field. Due to the rotation, the flux which links with the armature changes continuously. Therefore, according to Faraday’s law, an emf is induced in the armature. This produces an electric current through the galvanometer and the slip rings and brushes.
The generated EMF depends on the number of armature coil turns, magnetic field strength, and the speed of the rotating field.
Schematic Diagram:-
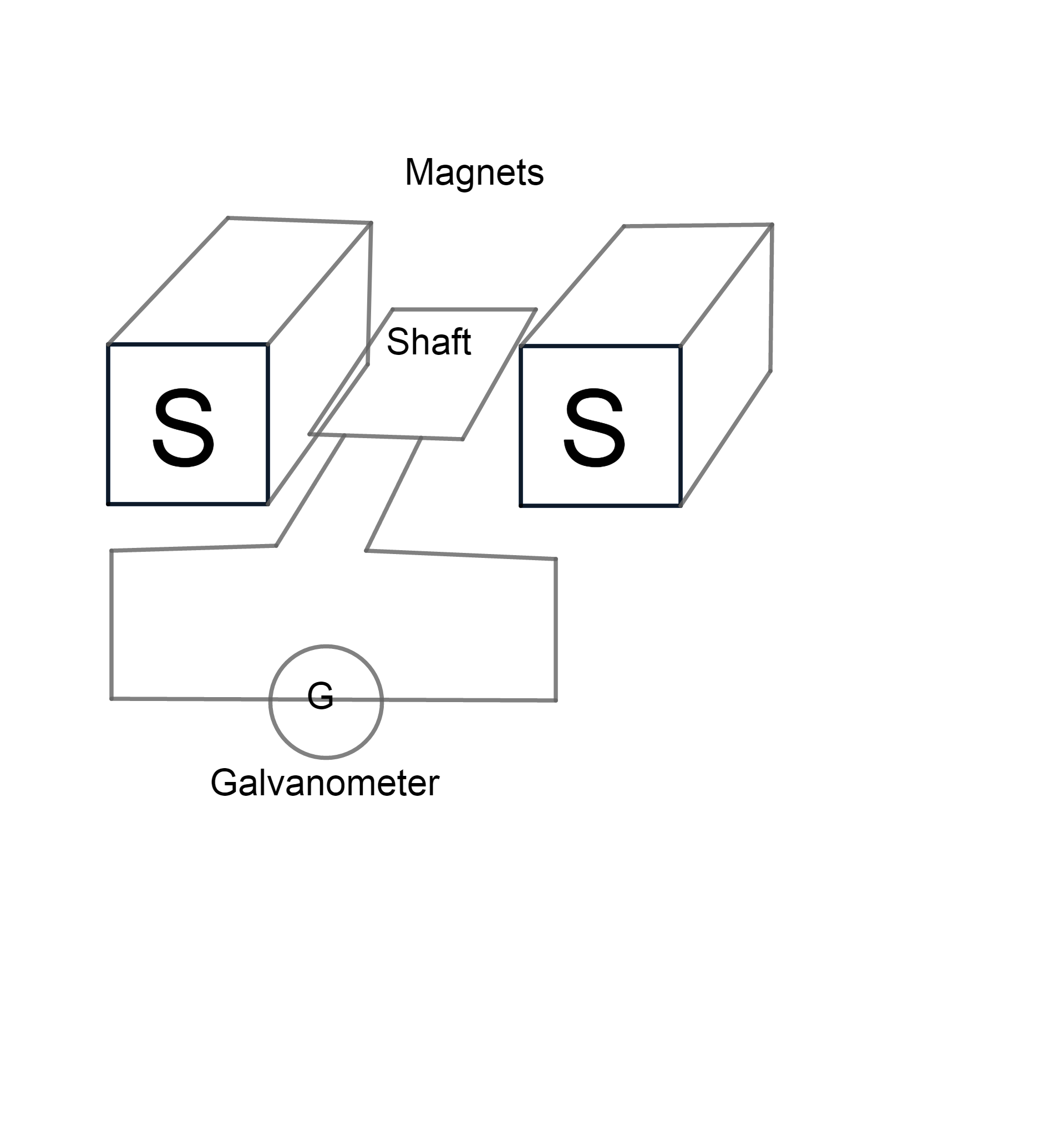
Change in direction of current:
When the shaft is perpendicular to direction of magnetic field, flux through the shaft is maximum. When it starts to rotate, flux through the shaft starts to reduce causing a current in the shaft, say in a positive direction. It will continue to produce a positive current till it reaches the parallel position (In parallel position flux is minimum). When the shaft moves from a perpendicular position to a parallel position, the increase in flux causes the generation of current in the opposite direction. In a continuously rotating shaft, the current will change its direction continuously
Note:
AC generators are the example of a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The mechanical energy supplied by the steam turbines, gas turbines, and combustion engines is converted into electrical energy in the form of sinusoidal alternating current.
Complete step by step answer:
Definition of Alternating current:-
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses its direction, and changes its magnitude continuously with time. However, in direct current (DC), it flows only in one direction.
AC Generator:-
AC generators are the device that produces alternating current. In the AC generators, an armature rotates between the poles of the magnet (which provide magnetic field) on an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field. Due to the rotation, the flux which links with the armature changes continuously. Therefore, according to Faraday’s law, an emf is induced in the armature. This produces an electric current through the galvanometer and the slip rings and brushes.
The generated EMF depends on the number of armature coil turns, magnetic field strength, and the speed of the rotating field.
Schematic Diagram:-

Change in direction of current:
When the shaft is perpendicular to direction of magnetic field, flux through the shaft is maximum. When it starts to rotate, flux through the shaft starts to reduce causing a current in the shaft, say in a positive direction. It will continue to produce a positive current till it reaches the parallel position (In parallel position flux is minimum). When the shaft moves from a perpendicular position to a parallel position, the increase in flux causes the generation of current in the opposite direction. In a continuously rotating shaft, the current will change its direction continuously
Note:
AC generators are the example of a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The mechanical energy supplied by the steam turbines, gas turbines, and combustion engines is converted into electrical energy in the form of sinusoidal alternating current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




