
Define and design a test cross.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: A test cross is known as a cross between an individual expressing a dominant trait with the one having its homozygous recessive trait in order to determine whether the dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous.
Complete answer:
A cross between an organism with unknown genotype and a recessive parent is known as test cross. It is considered as a way to explore the genotype of an organism. The test cross was used earlier as an experimental mating test to determine the presence of alleles in the genotype. The genetic makeup of an organism is called its genotype, and it reflects all of the alleles (forms of the gene), that are carried by the organism. Subsequently, a test cross can help to analyse whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific allele. If the progenies produced by a test cross express 50% dominant trait and 50% recessive trait, then it is confirmed that the unknown individual is heterozygous for the trait. On the other hand, if the progeny produces a dominant trait, then the unknown individual is homozygous for the trait.
Example:
When a tall plant (TT) is crossed with dwarf plant (tt), in the F1 generation only heterozygous tall plants (Tt) appear. When these plants are crossed with homozygous recessive (tt) or dwarf plants, it is known as test cross. In the diagram given below, a test cross between tall heterozygous F1 hybrid with dwarf homozygous recessive parent produces tall and dwarf in equal proportion demonstrating that F1 hybrids are heterozygous.
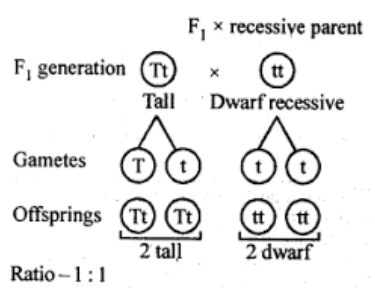
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: A test cross basically involves mating an unknown genotypic individual with a known homozygous recessive parent. This happens because recessive alleles will always be masked by the presence of dominant alleles. Hence the phenotype of any offspring will imitate the genotype of the unknown parent. It can be used to know whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous.
Complete answer:
A cross between an organism with unknown genotype and a recessive parent is known as test cross. It is considered as a way to explore the genotype of an organism. The test cross was used earlier as an experimental mating test to determine the presence of alleles in the genotype. The genetic makeup of an organism is called its genotype, and it reflects all of the alleles (forms of the gene), that are carried by the organism. Subsequently, a test cross can help to analyse whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific allele. If the progenies produced by a test cross express 50% dominant trait and 50% recessive trait, then it is confirmed that the unknown individual is heterozygous for the trait. On the other hand, if the progeny produces a dominant trait, then the unknown individual is homozygous for the trait.
Example:
When a tall plant (TT) is crossed with dwarf plant (tt), in the F1 generation only heterozygous tall plants (Tt) appear. When these plants are crossed with homozygous recessive (tt) or dwarf plants, it is known as test cross. In the diagram given below, a test cross between tall heterozygous F1 hybrid with dwarf homozygous recessive parent produces tall and dwarf in equal proportion demonstrating that F1 hybrids are heterozygous.

Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: A test cross basically involves mating an unknown genotypic individual with a known homozygous recessive parent. This happens because recessive alleles will always be masked by the presence of dominant alleles. Hence the phenotype of any offspring will imitate the genotype of the unknown parent. It can be used to know whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




