
Define and explain chain isomerism and position isomerism with example in each case.
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint :Isomerism is defined as the phenomenon which includes more than one compound which have the same chemical formula but the chemical structure is different. The chemical compounds which have identical chemical formulae but the difference is present in the properties and arrangement of the atoms in the molecule are called isomers. The word called ‘ isomer’ has been derived from the Greek words ‘isos’ and the other word ‘meros’ which has the meaning ‘ equal parts’.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The isomerism has been classified into structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. In structural isomerism we have the functional groups and atoms in the molecules of these isomers are linked in different ways. Whereas in stereoisomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the orientation of atoms belonging to the molecule in the three dimensional space.
The chain isomerism is the part of structural isomerism. It is also referred to as skeletal isomerism also. The components of such isomers tend to display differently branched structures. These structural isomers usually differ in the chain of carbon atoms. So the chain isomers differ in the arrangement of the carbon atom in a straight or branched chain of compounds. Let us take the example of pentane which shows chain isomerism
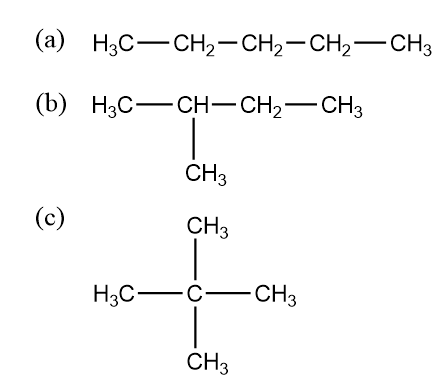
The name of a. The structure is pentane which is in a straight chain and no branching takes place. In part b. The structure is isopentane or $ 2 - {\text{methylbutane}} $ which is branched as it contains one branching methyl group. In structure c. neopentane or $ 2,2{\text{ dimethylpropane}} $ in this the structure is branched and is branched into 2 methyl groups.
The position isomerism is also the part of structural isomerism. In this the position of the functional groups or the substituent atoms are present in different isomers. So in this isomerism we see the attachment of the functional groups to other carbon atoms in the chain of carbon. Here we will take the example of chloropropane in which the position of the chlorine will be different as it will be attached to two different carbon in the compound.
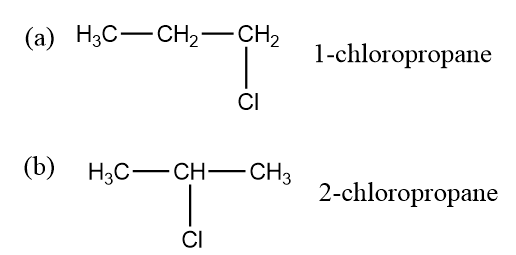
In the part (a) we see that the chlorine is attached to 3 rd carbon while in (b) part the chlorine is attached to the second carbon. So the position of the chlorine is different in both the cases which lead to position isomerism.
Note :
The other types of structural isomerism are functional isomerism, metamerism , tautomerism and ring chain isomerism. In functional isomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the functional groups attached are different. The metamerism arises because of the presence of the different alkyl chain which has been attached on each side of the functional group. In the ring chain isomerism we see that one isomer has the open chain structure while the other structure is ring type structure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The isomerism has been classified into structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. In structural isomerism we have the functional groups and atoms in the molecules of these isomers are linked in different ways. Whereas in stereoisomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the orientation of atoms belonging to the molecule in the three dimensional space.
The chain isomerism is the part of structural isomerism. It is also referred to as skeletal isomerism also. The components of such isomers tend to display differently branched structures. These structural isomers usually differ in the chain of carbon atoms. So the chain isomers differ in the arrangement of the carbon atom in a straight or branched chain of compounds. Let us take the example of pentane which shows chain isomerism

The name of a. The structure is pentane which is in a straight chain and no branching takes place. In part b. The structure is isopentane or $ 2 - {\text{methylbutane}} $ which is branched as it contains one branching methyl group. In structure c. neopentane or $ 2,2{\text{ dimethylpropane}} $ in this the structure is branched and is branched into 2 methyl groups.
The position isomerism is also the part of structural isomerism. In this the position of the functional groups or the substituent atoms are present in different isomers. So in this isomerism we see the attachment of the functional groups to other carbon atoms in the chain of carbon. Here we will take the example of chloropropane in which the position of the chlorine will be different as it will be attached to two different carbon in the compound.

In the part (a) we see that the chlorine is attached to 3 rd carbon while in (b) part the chlorine is attached to the second carbon. So the position of the chlorine is different in both the cases which lead to position isomerism.
Note :
The other types of structural isomerism are functional isomerism, metamerism , tautomerism and ring chain isomerism. In functional isomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the functional groups attached are different. The metamerism arises because of the presence of the different alkyl chain which has been attached on each side of the functional group. In the ring chain isomerism we see that one isomer has the open chain structure while the other structure is ring type structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




