
Define bandwidth of an amplifier.
Answer
527.6k+ views
Hint: An amplifier is a device used to convert a low voltage signal into a high voltage signal from a source device. In other words, it used to gain power. The Bandwidth (BW) of an amplifier is defined as the difference between the frequency limits of the amplifier.
Complete step by step answer:
The range of frequencies within a band is known as bandwidth.
An amplifier also known as an amp is an electronic device that enhances the power of a signal. It uses electric power to increase the amplitude of a signal at the initial input to produce a gradually enhanced amplitude signal at output.
The width of frequencies or the band of frequencies that an amplifier can amplify most effectively is represented using a bandwidth. An amplifier has frequencies which can be amplified, these frequencies have a lower limit (that could even be zero) and an upper limit but the amplitude enhancement cannot be done for all these frequencies effectively.
So if an amplifier is designed to amplify the frequencies between a lower frequency ${f_1}$ and a higher frequency ${f_2}$ the bandwidth will be the difference of these two frequencies. So the difference of ${f_2}$ and ${f_1}$ will be the bandwidth of the amplifier.
$BW = {f_2} - {f_1}$
The following image shows the graphical representation of bandwidth of an amplifier:
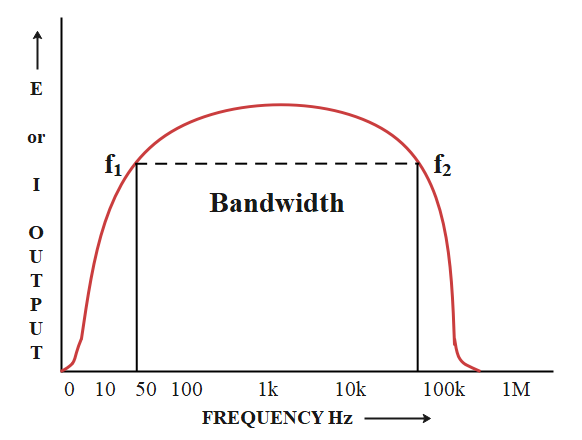
For example, if an amplifier is designed to amplify a frequency between 20 hertz and 15 kilohertz, the bandwidth will be 15 kilohertz minus 20 hertz, or 14,980 hertz (14,980 Hz).
Additional Information:
The spectrum of frequency that can be normally amplified by an amplifier is its bandwidth. So the useful frequency range is depicted by the bandwidth.
Bandwidth is given in Hertz or Hz (cycles per second).
The upper and lower limits of frequency are also known as half points.
Note: Bandwidth is used a lot in radios, telephones and other devices. A telephone uses 3 kHz band to carry understandable conversations. Regardless of the location of a band in the frequency spectrum, any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information.
Complete step by step answer:
The range of frequencies within a band is known as bandwidth.
An amplifier also known as an amp is an electronic device that enhances the power of a signal. It uses electric power to increase the amplitude of a signal at the initial input to produce a gradually enhanced amplitude signal at output.
The width of frequencies or the band of frequencies that an amplifier can amplify most effectively is represented using a bandwidth. An amplifier has frequencies which can be amplified, these frequencies have a lower limit (that could even be zero) and an upper limit but the amplitude enhancement cannot be done for all these frequencies effectively.
So if an amplifier is designed to amplify the frequencies between a lower frequency ${f_1}$ and a higher frequency ${f_2}$ the bandwidth will be the difference of these two frequencies. So the difference of ${f_2}$ and ${f_1}$ will be the bandwidth of the amplifier.
$BW = {f_2} - {f_1}$
The following image shows the graphical representation of bandwidth of an amplifier:

For example, if an amplifier is designed to amplify a frequency between 20 hertz and 15 kilohertz, the bandwidth will be 15 kilohertz minus 20 hertz, or 14,980 hertz (14,980 Hz).
Additional Information:
The spectrum of frequency that can be normally amplified by an amplifier is its bandwidth. So the useful frequency range is depicted by the bandwidth.
Bandwidth is given in Hertz or Hz (cycles per second).
The upper and lower limits of frequency are also known as half points.
Note: Bandwidth is used a lot in radios, telephones and other devices. A telephone uses 3 kHz band to carry understandable conversations. Regardless of the location of a band in the frequency spectrum, any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




