
Define capacitive reactance. Write its SI unit.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: A good capacitor completely blocks the passage of direct current (DC) through it but allows alternating current (AC) to pass through it. Reactance is the opposition to the current flow of an element in the circuit because of its capacitance. Its unit is similar to the unit of resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
It allows alternating current (AC) to flow through the external circuit in one direction and then in the opposite direction at a frequency which is equal to the frequency of applied voltage. But after some time, capacitive reactance also opposes the passage of alternating current (AC) like resistance. The measurement of capacitive reactance is also taken in ohms. But reactance of capacitors is more complex than resistance because of the electrical signal frequency. The capacitive reactance is denoted by Xc and given by the formula,
${ X }_{ c }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2\pi fc }$ = $\dfrac { 0.159 }{ fC }$
Where ‘f’ is equal to frequency of the signal and ‘c’ is the capacitance of the capacitor.
Capacitive reactance varies inversely with respect to the applied voltage frequency. If the frequency is higher, the capacitance is less. And in the same way, if frequency is lesser, the capacitance is higher.
The capacitor blocks direct current because for a DC voltage f = 0, Xc = 1/0 = ∞.
The S.I unit of capacitance is farad, but the S.I unit of capacitive reactance is ohms. It does not have a fixed value like resistance but keeps varying according to the applied frequency. A complex impedance is found due to the presence of electrons in the form of charges on the capacitor plates passing from one to another rapidly.
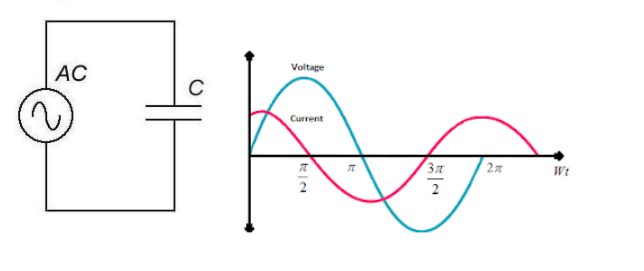
Note: A capacitor in the circuit retards current flow by causing the alternating voltage to lag behind the alternating current (AC) and the measurement of this opposition is called the reactance. This forms the complex impedance of the capacitor.
Complete step by step answer:
It allows alternating current (AC) to flow through the external circuit in one direction and then in the opposite direction at a frequency which is equal to the frequency of applied voltage. But after some time, capacitive reactance also opposes the passage of alternating current (AC) like resistance. The measurement of capacitive reactance is also taken in ohms. But reactance of capacitors is more complex than resistance because of the electrical signal frequency. The capacitive reactance is denoted by Xc and given by the formula,
${ X }_{ c }=\dfrac { 1 }{ 2\pi fc }$ = $\dfrac { 0.159 }{ fC }$
Where ‘f’ is equal to frequency of the signal and ‘c’ is the capacitance of the capacitor.
Capacitive reactance varies inversely with respect to the applied voltage frequency. If the frequency is higher, the capacitance is less. And in the same way, if frequency is lesser, the capacitance is higher.
The capacitor blocks direct current because for a DC voltage f = 0, Xc = 1/0 = ∞.
The S.I unit of capacitance is farad, but the S.I unit of capacitive reactance is ohms. It does not have a fixed value like resistance but keeps varying according to the applied frequency. A complex impedance is found due to the presence of electrons in the form of charges on the capacitor plates passing from one to another rapidly.

Note: A capacitor in the circuit retards current flow by causing the alternating voltage to lag behind the alternating current (AC) and the measurement of this opposition is called the reactance. This forms the complex impedance of the capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




