
Define coelom. Explain the two types of coelom formation in animals.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: It is also an important characteristic for the animal classification. On the basis of the presence or absence of body cavity, animals are classified into different groups.
Complete answer:
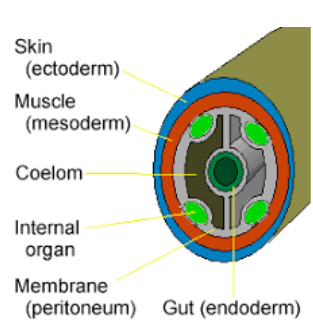
The coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity present on animals who developed from three layers of tissues during their embryonic stages. These types of animals are called metazoans. Ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm are the three layers. The coelom is the body cavity located between the body wall and the gut wall. The coelom is lined or made from mesodermal epithelium cells. Based on the presence or absence of the body cavity, the animals are categorized into coelomates, pseudocoelomates and acoelomates.
Coelomates are those animals or organisms that possess a true coelom or body cavity. In this case, the coelom is lined by mesodermal epithelium. They are further divided into two sub-categories: protostomes and deuterostomes based on the position of blastopore and coelom formation.
Pseudocoelomates are those animals where the body cavity is partially lined by mesoderm cells.
Acoelomates are those animals where coelom are absent.
There are two different processes by which coelom is formed. They are schizocoelom and enterocoelom.
Schizocoelom- This mechanism of development of coelom is found in protostomes. In this case, the coelom is developed by splitting of mesoderm. During splitting of mesoderm, the one part is attached to the ectoderm and the other end is attached to the endoderm. The cavity produced between them is called coelom. The animals included in this are Arthropoda, Annelida, and Mollusca.
Enterocoelom – This type of mechanism is found in deuterostomes. This coelom is formed by the outgrowth/pocket of the archenteron. Finally, these pockets fused together and formed coelom. These types of coelom formation are seen in echinoderms and chordates.
Note: The functions of the coelom are –
> It acts as a shock absorber – it protects from mechanical shock.
> Hydrostatic skeleton – helps in movements of soft body organisms.
> They also support the immune system.
> Helps in gases transportation
Complete answer:

The coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity present on animals who developed from three layers of tissues during their embryonic stages. These types of animals are called metazoans. Ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm are the three layers. The coelom is the body cavity located between the body wall and the gut wall. The coelom is lined or made from mesodermal epithelium cells. Based on the presence or absence of the body cavity, the animals are categorized into coelomates, pseudocoelomates and acoelomates.
Coelomates are those animals or organisms that possess a true coelom or body cavity. In this case, the coelom is lined by mesodermal epithelium. They are further divided into two sub-categories: protostomes and deuterostomes based on the position of blastopore and coelom formation.
Pseudocoelomates are those animals where the body cavity is partially lined by mesoderm cells.
Acoelomates are those animals where coelom are absent.
There are two different processes by which coelom is formed. They are schizocoelom and enterocoelom.
Schizocoelom- This mechanism of development of coelom is found in protostomes. In this case, the coelom is developed by splitting of mesoderm. During splitting of mesoderm, the one part is attached to the ectoderm and the other end is attached to the endoderm. The cavity produced between them is called coelom. The animals included in this are Arthropoda, Annelida, and Mollusca.
Enterocoelom – This type of mechanism is found in deuterostomes. This coelom is formed by the outgrowth/pocket of the archenteron. Finally, these pockets fused together and formed coelom. These types of coelom formation are seen in echinoderms and chordates.
Note: The functions of the coelom are –
> It acts as a shock absorber – it protects from mechanical shock.
> Hydrostatic skeleton – helps in movements of soft body organisms.
> They also support the immune system.
> Helps in gases transportation
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




