
Define ‘drift velocity’ of electrons in a conductor.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint:A conductor contains electrons and flow of electrons constitutes a current. When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, electrons feel a push towards the positive terminal of the battery and travel with a velocity called drift velocity and current is produced.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define drift velocity as the velocity acquired by electrons or other charge carriers when an external electric field is applied to a conductor. When no external potential difference or electric field is applied, an electron inside a conductor can have any velocity due to thermal energy inside the conductor and they move around in random directions, due to which we get an average velocity equal to zero. When an external electric field is applied to the conductor, the electrons are forced to flow in one direction; this is called ‘drifting’ in the direction of the field.
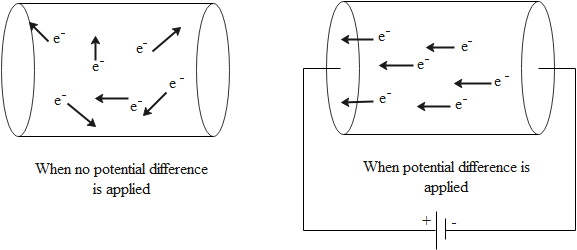
Drift velocity acquired by electrons is directly proportional to electric field applied to the conductor. We can also explain Ohm's law in terms of drift velocity. Current is given in terms of drift velocity by the following expression:
\[I = {{\text{v}}_d}enA\]
where I is the current flowing through the conductor, denotes the drift velocity attained by electrons, e is the charge on the electrons, n represents the number density of electrons while A represents the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Note: When potential difference is applied the electrons drift towards the positive terminal of the battery. But we take the direction of the conventional current to be opposite to that of the direction of drift of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define drift velocity as the velocity acquired by electrons or other charge carriers when an external electric field is applied to a conductor. When no external potential difference or electric field is applied, an electron inside a conductor can have any velocity due to thermal energy inside the conductor and they move around in random directions, due to which we get an average velocity equal to zero. When an external electric field is applied to the conductor, the electrons are forced to flow in one direction; this is called ‘drifting’ in the direction of the field.

Drift velocity acquired by electrons is directly proportional to electric field applied to the conductor. We can also explain Ohm's law in terms of drift velocity. Current is given in terms of drift velocity by the following expression:
\[I = {{\text{v}}_d}enA\]
where I is the current flowing through the conductor, denotes the drift velocity attained by electrons, e is the charge on the electrons, n represents the number density of electrons while A represents the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Note: When potential difference is applied the electrons drift towards the positive terminal of the battery. But we take the direction of the conventional current to be opposite to that of the direction of drift of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




