
Define linear charge density and surface charge density at a point.
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The charge density is a value of charge accumulation per unit length or a surface area or a volume. So the linear charge distribution shows how charges are distributed along a length. The surface charge distribution shows how charges are distributed across an area A.
Complete step by step solution:
As I mentioned in the hint, the charge density is the value of charged particles per unit length, surface area or volume, so we can consider it as a continuous charge distribution along a length, surface area or volume. The charge density will be the same for every point on a body having continuous charge distribution.
Linear charge density: Linear charge density at a point on a linear line of charge is defined as the charge distributed per unit length. We can define linear charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small length of $dl$. Its unit is $\text{coulomb/metre (C/m)}$. Linear charge density is denoted by the Greek letter lambda $\left( \lambda \right)$.
$\text{Linear Charge Density (}\lambda \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dl}$
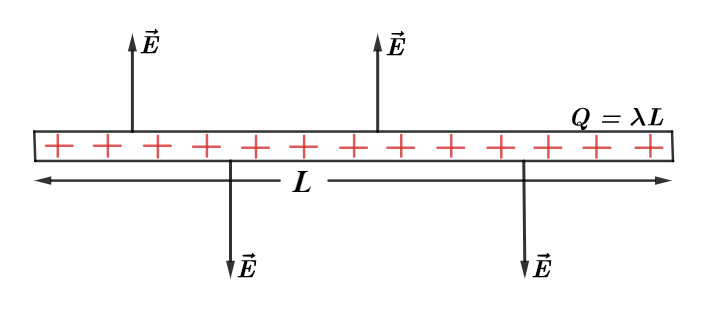
Given above is an example of positive linear charge density of a rod of length L whose linear charge density is expressed as $\lambda $. There is a positive charge distribution present along the length of the rod of length L and the electric field is normal to the length of the rod and is directed outwards.
Surface charge density: Surface charge density at a point on a charged surface is defined as the charge distributed per unit area. We can define surface charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small area $dA$. Its unit is $\text{coulomb/meter}{{\text{e}}^{2}}\text{ (C/}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\text{)}$. Surface charge density is denoted by the Greek symbol sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$.
$\text{Surface Charge Density(}\sigma \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dA}$
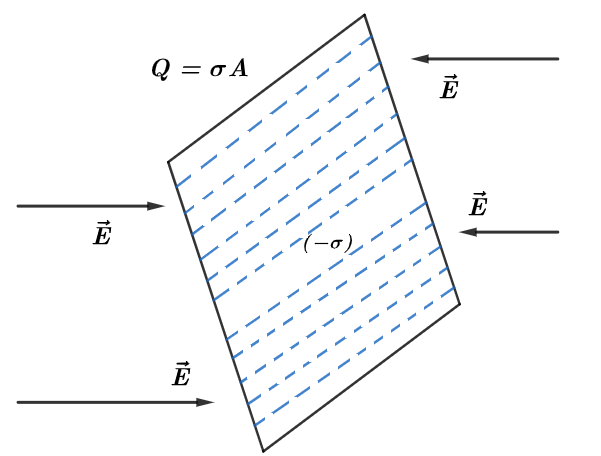
Given above is a negatively charged sheet of surface area A and a surface charge density of $\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }$. The negative sign indicates that the charge distribution is negative and electric fields are directed toward the charged sheet.
Note::
(i)The surface charge density can be positive or negative depending on the charge distribution.
(ii)There is also volume charge density, which is defined as the charge distributed per unit volume. We can define volume charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small volume $dV$.
(iii)Its unit is $\text{coulomb/meter}{{\text{e}}^{3}}\text{ (C/}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\text{)}$. Surface charge density is denoted by the Greek symbol rho $\left( \rho \right)$.
$\text{Volume Charge Density(}\rho \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dV}$
Complete step by step solution:
As I mentioned in the hint, the charge density is the value of charged particles per unit length, surface area or volume, so we can consider it as a continuous charge distribution along a length, surface area or volume. The charge density will be the same for every point on a body having continuous charge distribution.
Linear charge density: Linear charge density at a point on a linear line of charge is defined as the charge distributed per unit length. We can define linear charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small length of $dl$. Its unit is $\text{coulomb/metre (C/m)}$. Linear charge density is denoted by the Greek letter lambda $\left( \lambda \right)$.
$\text{Linear Charge Density (}\lambda \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dl}$

Given above is an example of positive linear charge density of a rod of length L whose linear charge density is expressed as $\lambda $. There is a positive charge distribution present along the length of the rod of length L and the electric field is normal to the length of the rod and is directed outwards.
Surface charge density: Surface charge density at a point on a charged surface is defined as the charge distributed per unit area. We can define surface charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small area $dA$. Its unit is $\text{coulomb/meter}{{\text{e}}^{2}}\text{ (C/}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\text{)}$. Surface charge density is denoted by the Greek symbol sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$.
$\text{Surface Charge Density(}\sigma \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dA}$

Given above is a negatively charged sheet of surface area A and a surface charge density of $\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }$. The negative sign indicates that the charge distribution is negative and electric fields are directed toward the charged sheet.
Note::
(i)The surface charge density can be positive or negative depending on the charge distribution.
(ii)There is also volume charge density, which is defined as the charge distributed per unit volume. We can define volume charge density as the ratio of a small charge $dq$ distributed over a small volume $dV$.
(iii)Its unit is $\text{coulomb/meter}{{\text{e}}^{3}}\text{ (C/}{{\text{m}}^{3}}\text{)}$. Surface charge density is denoted by the Greek symbol rho $\left( \rho \right)$.
$\text{Volume Charge Density(}\rho \text{)}=\dfrac{dq}{dV}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




