
Define linkage.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: In Mendel's law of inheritance, he suggested the theory of independent inheritance. The linkage concept was a deviation from Mendel's theory and was observed by some British geneticists in 1905.
Complete answer:
The DNA sequences which are close together on a chromosome tend to be inherited together during sexual reproduction, in the meiosis phase. This tendency of the sequences is known as linkage and the sequence is said to be linked. It is the most prominent exception to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment.
Additional Information:
Linkage, along with recombination, describes the inheritance of genes. According to Mendel's law, crossing over two genes of a character should divide. But Morgan noted that the close-set of two genes didn't follow this rule and gets inherited together. These two genes are located in the same chromosomes and are tied to each other. The loose linkages give a greater chance of recommendation but the powerful ones give very limited chances for this.
There are mainly two types of linkage- complete and incomplete. In the case of complete linkage two or more traits are inherited and surface in two or more generations in their original combination. These genes are located nearby in the same chromosome. On the other hand, in an incomplete one, some portions of genes are non-parental and situated at a distance on the chromosome. An example of complete linkage is the grey body and long wings genes of male drosophila.
Note: According to Mendel, the inheritance of every trait is independent of every other trait. But in the rediscovery of his work, an exception was found by the British geneticist William Bateson, Edith Rebecca Saunders, and Reginal Punnett. When they studied two genes of the pea plant- the one for flower color and the other for the shape of pollen grains, they surprisingly discovered the theory of linkage where the genes inherited together instead of inheriting independently.
Here’s a diagram showing linkage:
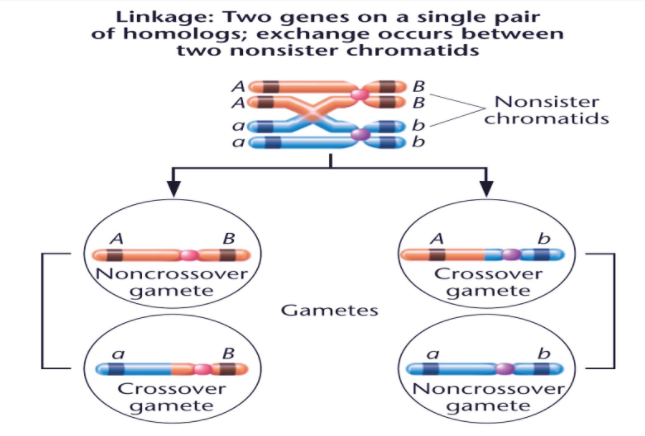
Complete answer:
The DNA sequences which are close together on a chromosome tend to be inherited together during sexual reproduction, in the meiosis phase. This tendency of the sequences is known as linkage and the sequence is said to be linked. It is the most prominent exception to Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment.
Additional Information:
Linkage, along with recombination, describes the inheritance of genes. According to Mendel's law, crossing over two genes of a character should divide. But Morgan noted that the close-set of two genes didn't follow this rule and gets inherited together. These two genes are located in the same chromosomes and are tied to each other. The loose linkages give a greater chance of recommendation but the powerful ones give very limited chances for this.
There are mainly two types of linkage- complete and incomplete. In the case of complete linkage two or more traits are inherited and surface in two or more generations in their original combination. These genes are located nearby in the same chromosome. On the other hand, in an incomplete one, some portions of genes are non-parental and situated at a distance on the chromosome. An example of complete linkage is the grey body and long wings genes of male drosophila.
Note: According to Mendel, the inheritance of every trait is independent of every other trait. But in the rediscovery of his work, an exception was found by the British geneticist William Bateson, Edith Rebecca Saunders, and Reginal Punnett. When they studied two genes of the pea plant- the one for flower color and the other for the shape of pollen grains, they surprisingly discovered the theory of linkage where the genes inherited together instead of inheriting independently.
Here’s a diagram showing linkage:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




