
Define magnetic ‘declination’ and ‘dip’ at a place.
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: If you tie the centre of a permanent magnet with a string and let it rotate freely around the axis, we can determine the magnetic ‘declination’ and ‘dip’ at that place. The terminologies are self-explanatory.
Complete answer:
Both magnetic ‘declination’ and ‘dip’ can be observed if you let a permanent magnet move freely around its axis. Let's first look at the Magnetic Declination.
Magnetic Declination:
Magnetic Declination is the angle between the direction of the true geographical north pole and the magnetic north pole from that place. True North pole is the actual geographical north pole and Magnetic north pole is the north pole towards which the permanent magnet would point. There is a small difference in the direction and this deviation changes from place to place. It happens because the magnetic north pole never stays constant.
If the magnet points towards the east of the actual north pole, then the declination is positive. If the magnet towards the west, then the declination is negative.
The following figure clearly shows the declination of a magnet.
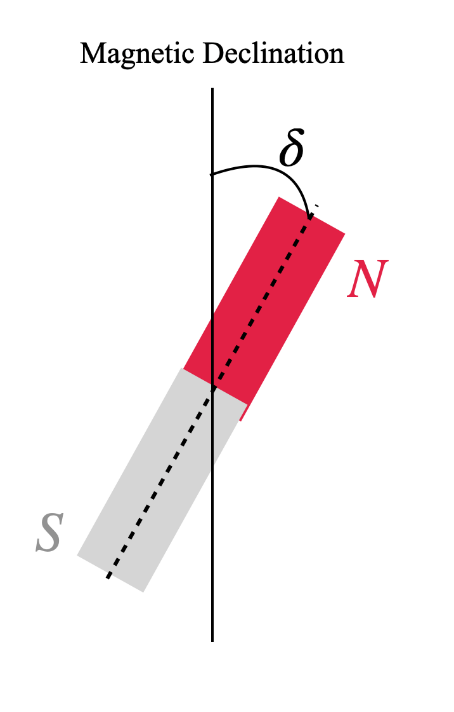
Magnetic Dip:
Now, let us look at the Magnetic Dip.
Magnetic dip is the angle the magnet would form with the horizontal. It is basically the angle between the magnetic fields at that place and the horizontal line. The dip angle or magnetic inclination is considered to be positive if the magnet is pointing downwards and negative if it is pointing upwards.
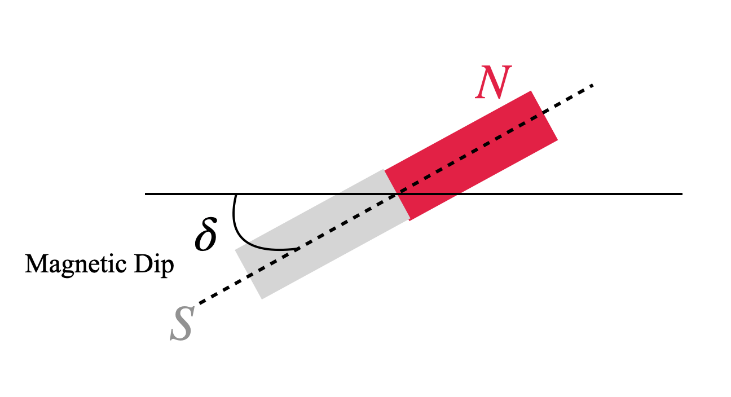
Note:
You can determine both of these quantities accurately if you have correct measuring tools. This gives us a clear idea about the magnetic fields of the earth. It changes continuously and follows a repeating pattern through the years. Solar flares can change the magnetic fields significantly and you can observe this using these two quantities.
Complete answer:
Both magnetic ‘declination’ and ‘dip’ can be observed if you let a permanent magnet move freely around its axis. Let's first look at the Magnetic Declination.
Magnetic Declination:
Magnetic Declination is the angle between the direction of the true geographical north pole and the magnetic north pole from that place. True North pole is the actual geographical north pole and Magnetic north pole is the north pole towards which the permanent magnet would point. There is a small difference in the direction and this deviation changes from place to place. It happens because the magnetic north pole never stays constant.
If the magnet points towards the east of the actual north pole, then the declination is positive. If the magnet towards the west, then the declination is negative.
The following figure clearly shows the declination of a magnet.

Magnetic Dip:
Now, let us look at the Magnetic Dip.
Magnetic dip is the angle the magnet would form with the horizontal. It is basically the angle between the magnetic fields at that place and the horizontal line. The dip angle or magnetic inclination is considered to be positive if the magnet is pointing downwards and negative if it is pointing upwards.

Note:
You can determine both of these quantities accurately if you have correct measuring tools. This gives us a clear idea about the magnetic fields of the earth. It changes continuously and follows a repeating pattern through the years. Solar flares can change the magnetic fields significantly and you can observe this using these two quantities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




