
Define Metagenesis. Give a suitable example
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: In some lower animals and plants, the parent body of an organism undergoes specific changes that are both structural and functional. These changes are also termed as alternation of generations. This is seen in organisms like Obelia which belong to the phylum Cnidaria.
Complete answer:
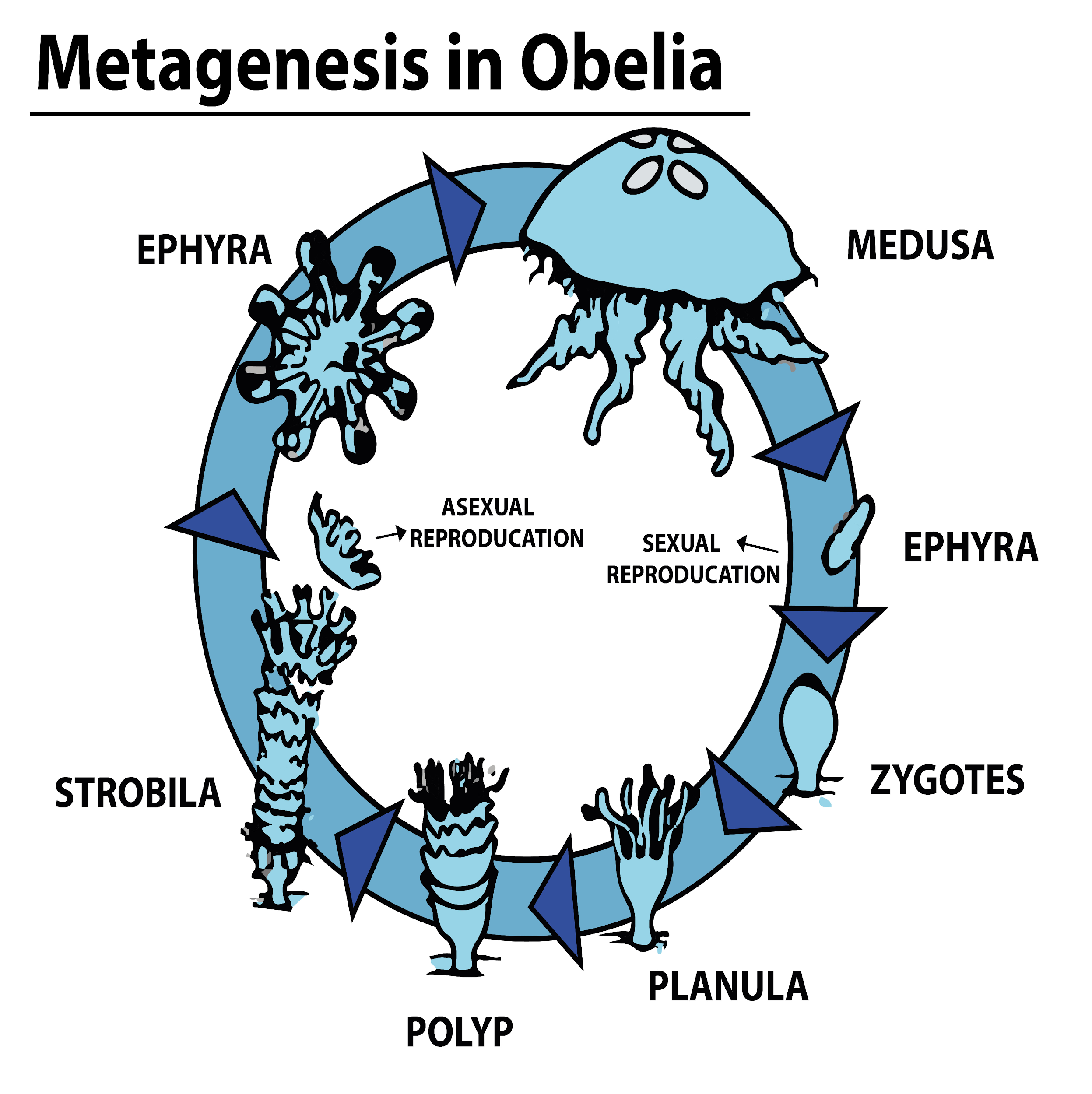
In some organisms, the diploid generation of the organism(sporophyte) changes into the haploid generation or the gamete producing body (gametophyte), and the gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into the sporophyte. This cycle is known as the alternation of generations or metagenesis. Metagenesis is shown by organisms belonging to the phylum Cnidaria and some algae, fungi, mosses, ferns, and seed plants.
Metagenesis in the animal kingdom:
Cnidarians exhibit two forms in their life cycle - the polyp form and medusa form. Polyps are the sporophytes and produce medusae asexually, while the medusae forms are the gametophytes which produce the polyps sexually
Example - Obelia.
Metagenesis in Plant kingdom:
In algae, mosses, ferns, seed plants, and fungi, alternation of generations are common. The sexual phase, called the gametophyte (haploid), produces gametes, and the asexual phase, or sporophyte (diploid), produces asexual spores.
Note:
The alternation of generations is most often referring to plants. Most plants that we see today spend the most time in their asexual phase. The structures that we know as ferns, trees, and flowers are the asexually reproducing structures of the plant. The plants only sexually reproduce to produce new plants that grow into new trees, flowers, and ferns.
Among the animals, many invertebrates show an alternation of sexual and asexual forms, but the alternation of haploid and diploid generations is unknown.
Complete answer:
In some organisms, the diploid generation of the organism(sporophyte) changes into the haploid generation or the gamete producing body (gametophyte), and the gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into the sporophyte. This cycle is known as the alternation of generations or metagenesis. Metagenesis is shown by organisms belonging to the phylum Cnidaria and some algae, fungi, mosses, ferns, and seed plants.
Metagenesis in the animal kingdom:
Cnidarians exhibit two forms in their life cycle - the polyp form and medusa form. Polyps are the sporophytes and produce medusae asexually, while the medusae forms are the gametophytes which produce the polyps sexually
Example - Obelia.
Metagenesis in Plant kingdom:
In algae, mosses, ferns, seed plants, and fungi, alternation of generations are common. The sexual phase, called the gametophyte (haploid), produces gametes, and the asexual phase, or sporophyte (diploid), produces asexual spores.

Note:
The alternation of generations is most often referring to plants. Most plants that we see today spend the most time in their asexual phase. The structures that we know as ferns, trees, and flowers are the asexually reproducing structures of the plant. The plants only sexually reproduce to produce new plants that grow into new trees, flowers, and ferns.
Among the animals, many invertebrates show an alternation of sexual and asexual forms, but the alternation of haploid and diploid generations is unknown.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




