
Define Peltier coefficient.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: The thermocouple is a sensor which is used to measure the temperature. This sensor consists of two non-similar metal wires, joined at one end, and connected to another thermocouple capable device at the other end. There is some amount of heat absorbed or evolved at the junctions on flow of current and its rate is Peltier coefficient.
Complete step by step answer:
Peltier coefficient- This is the amount of heat energy absorbed or evolved at one of the junctions of a thermocouple when one ampere current flows for one second. A thermocouple is a sensor that is used for measuring the temperature. Thermocouples consist of two wire legs made from different metals. The wires legs are wedded together at one end, for creating a junction. This junction is a point where the temperature is measured. When the junction experiences a change in temperature, a voltage is created. Let us consider a thermocouple formed by two types of wire, `Type A wire’ and `Type B wire’ with hot junction (H) and cold junction (C and
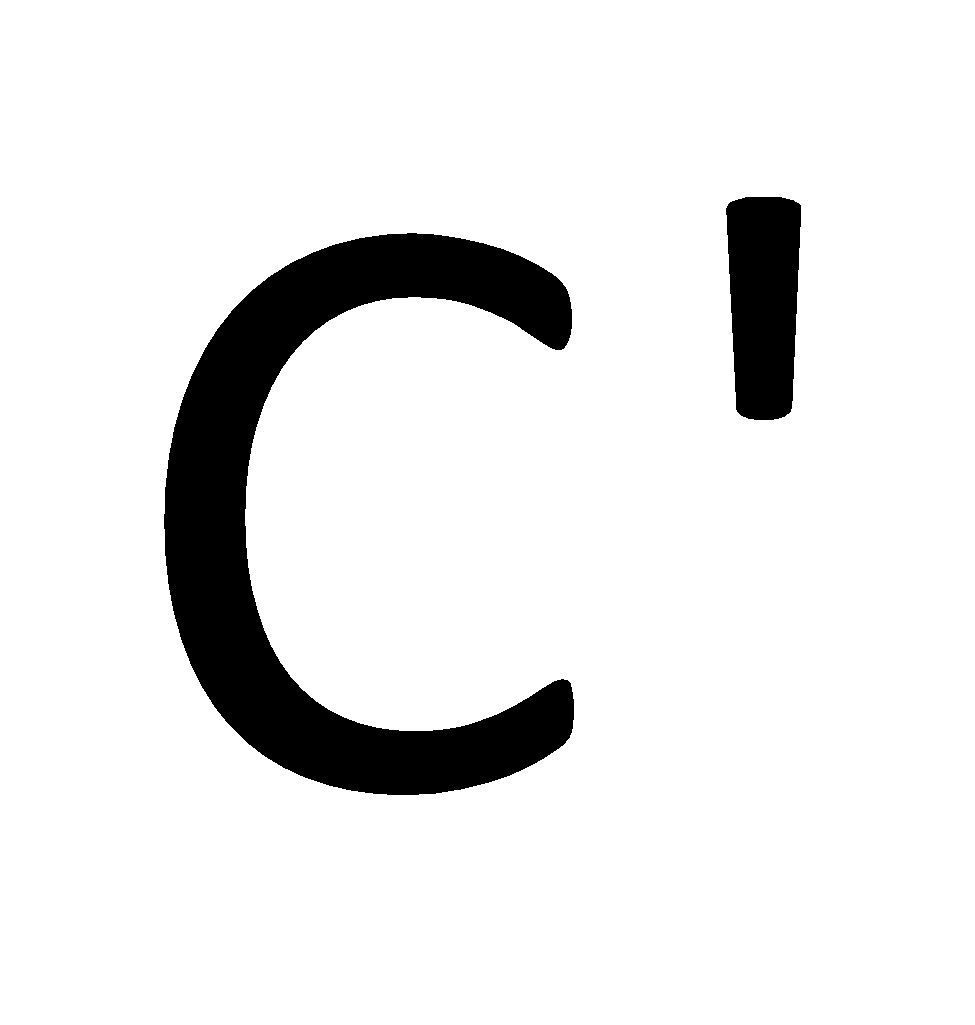 ).
).
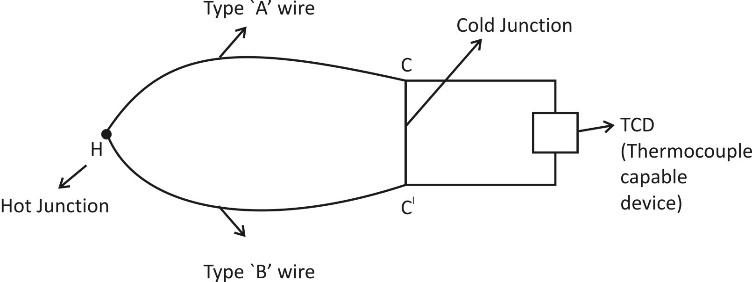
If `I’ ampere current is flowing throughout the thermocouple for time `t’ and due to this, the heat evolved or absorbed at one of the junctions in thermocouple is `Q’, then the Peltier coefficient `P’ is given by the relation:
$P = \dfrac{Q}{{It}}$
Note:
1. The thermocouple is used for both the AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) measurements.
2. The Peltier coefficient is the phenomenon that a potential difference applied across the TC (Thermocouple) causes a temperature difference between the junctions of the different materials in the TC (Thermocouple). This effect is opposite to the seebeck effect.
Complete step by step answer:
Peltier coefficient- This is the amount of heat energy absorbed or evolved at one of the junctions of a thermocouple when one ampere current flows for one second. A thermocouple is a sensor that is used for measuring the temperature. Thermocouples consist of two wire legs made from different metals. The wires legs are wedded together at one end, for creating a junction. This junction is a point where the temperature is measured. When the junction experiences a change in temperature, a voltage is created. Let us consider a thermocouple formed by two types of wire, `Type A wire’ and `Type B wire’ with hot junction (H) and cold junction (C and
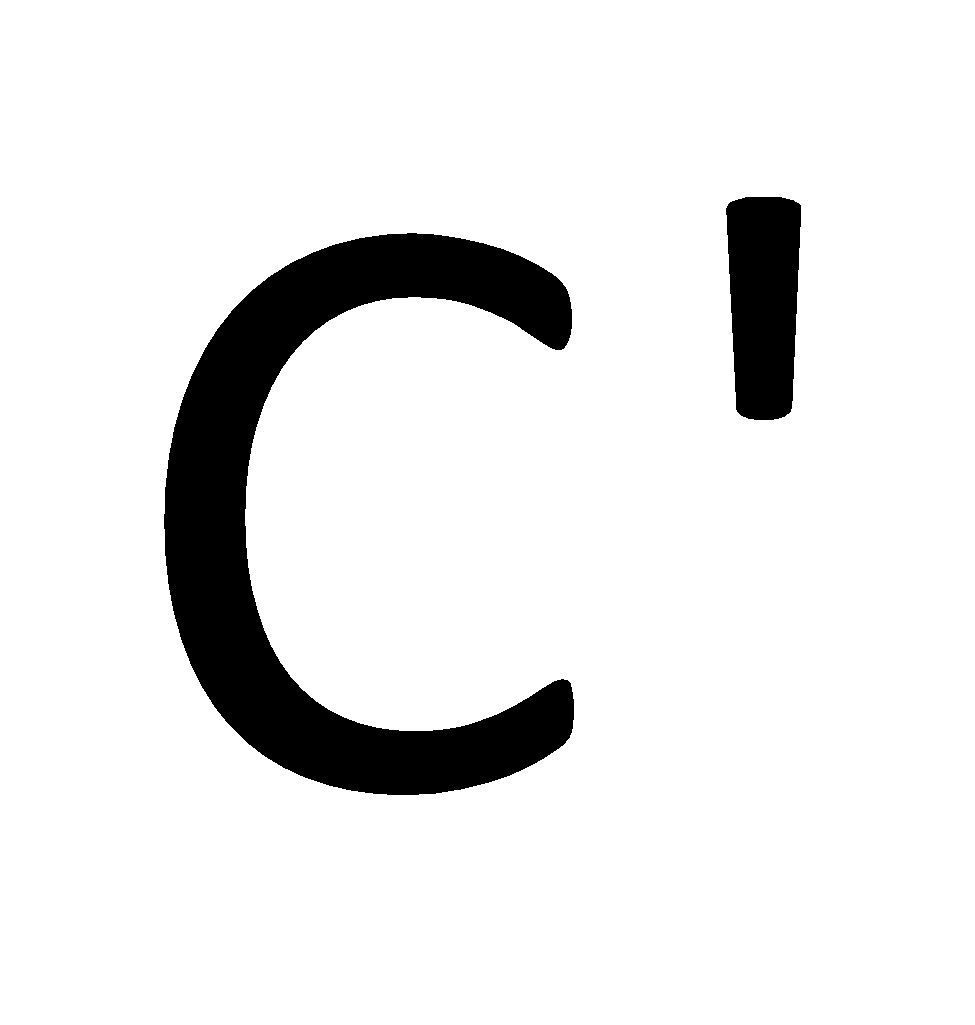

If `I’ ampere current is flowing throughout the thermocouple for time `t’ and due to this, the heat evolved or absorbed at one of the junctions in thermocouple is `Q’, then the Peltier coefficient `P’ is given by the relation:
$P = \dfrac{Q}{{It}}$
Note:
1. The thermocouple is used for both the AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) measurements.
2. The Peltier coefficient is the phenomenon that a potential difference applied across the TC (Thermocouple) causes a temperature difference between the junctions of the different materials in the TC (Thermocouple). This effect is opposite to the seebeck effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the advantages of vegetative propagation class 12 biology CBSE

Suicide bags of cells are aEndoplasmic reticulum bLysosome class 12 biology CBSE

What is the Full Form of PVC, PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP and PS ?




