
Define principal focus of a plane mirror.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Before going to a plane mirror, first understand the definitions for a spherical mirror. Then we can consider a plane mirror as a spherical mirror with infinite radius and interpret the corresponding data.
Formula used:
$f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let first understand the meaning of principal focus for a curved mirror.
The most common type of curved mirror is a spherical mirror. A spherical mirror has the shape of a section from the surface of a hollow sphere. If the inside surface of the mirror is polished, it is a concave mirror. If the outside is polished, it is a convex mirror.
Let us understand a few definitions of a spherical mirror.
1) Pole (P) : It is the midpoint in the mirror.
2) Centre of curvature (C) : It is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part.
3) Radius of curvature (R) : It is the distance between the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature.
4) Principal axis : A line passing through P and C i.e. pole and the centre of curvature.
5) Focus (F) ; It is an image point on the principal axis for which the object is at infinity.
6) Focal length (f) : It is the distance between the pole and focus of the mirror (P and f). Focal length (f) is half of the radius of curvature i.e. $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$.
7) Power : It is the converging or diverging ability of the mirror.
8) Aperture : It is the effective diameter of the light reflecting area. Intensity of image is directly proportional to the area, which is directly proportional to the square of the aperture.
9) Focal plane : A plane passing from the focus and perpendicular to the principal axis.
The formula of the positions of the object and its image is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ , where f is the focal length of the mirror.
A plane mirror can also be considered as a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is infinite and the centre of curvature will lie at infinite distance.
Therefore, the focal length of a plane mirror will be equal to $f=\dfrac{R}{2}=\dfrac{\infty }{2}=\infty $.
Hence, the focus of a plane mirror is at infinity.
When parallel rays of light fall on a concave mirror:
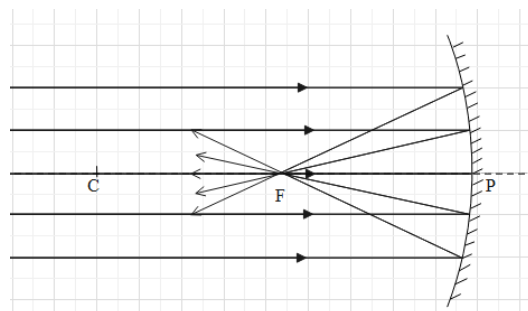
When parallel rays of light fall on a convex mirror:
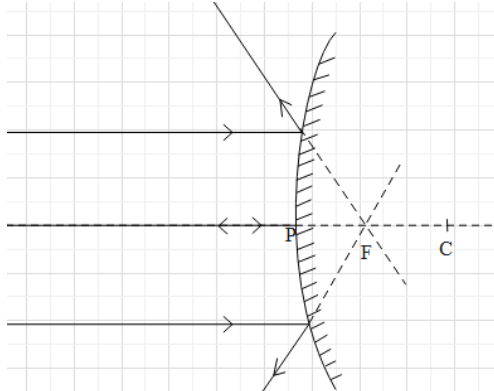
When parallel rays of light fall on a plane mirror.
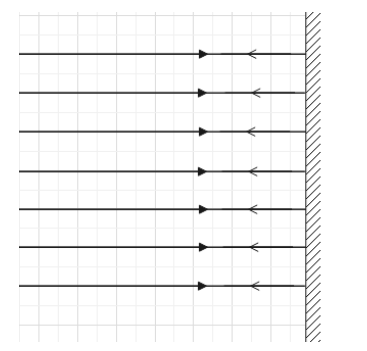
Note: Focus of a mirror is defined as the point where all the light rays parallel to the principal axis intersect after reflecting from the surface of the mirror.
In case of a plane mirror, the parallel light rays will hit the mirror such that they are perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. Therefore, they will travel the same path but in opposite directions. Hence, we can say that these rays will meet at infinity.
Therefore, the focus of a plane mirror is at infinity.
Formula used:
$f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let first understand the meaning of principal focus for a curved mirror.
The most common type of curved mirror is a spherical mirror. A spherical mirror has the shape of a section from the surface of a hollow sphere. If the inside surface of the mirror is polished, it is a concave mirror. If the outside is polished, it is a convex mirror.
Let us understand a few definitions of a spherical mirror.
1) Pole (P) : It is the midpoint in the mirror.
2) Centre of curvature (C) : It is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part.
3) Radius of curvature (R) : It is the distance between the pole of the mirror and the centre of curvature.
4) Principal axis : A line passing through P and C i.e. pole and the centre of curvature.
5) Focus (F) ; It is an image point on the principal axis for which the object is at infinity.
6) Focal length (f) : It is the distance between the pole and focus of the mirror (P and f). Focal length (f) is half of the radius of curvature i.e. $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$.
7) Power : It is the converging or diverging ability of the mirror.
8) Aperture : It is the effective diameter of the light reflecting area. Intensity of image is directly proportional to the area, which is directly proportional to the square of the aperture.
9) Focal plane : A plane passing from the focus and perpendicular to the principal axis.
The formula of the positions of the object and its image is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ , where f is the focal length of the mirror.
A plane mirror can also be considered as a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is infinite and the centre of curvature will lie at infinite distance.
Therefore, the focal length of a plane mirror will be equal to $f=\dfrac{R}{2}=\dfrac{\infty }{2}=\infty $.
Hence, the focus of a plane mirror is at infinity.
When parallel rays of light fall on a concave mirror:

When parallel rays of light fall on a convex mirror:

When parallel rays of light fall on a plane mirror.

Note: Focus of a mirror is defined as the point where all the light rays parallel to the principal axis intersect after reflecting from the surface of the mirror.
In case of a plane mirror, the parallel light rays will hit the mirror such that they are perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. Therefore, they will travel the same path but in opposite directions. Hence, we can say that these rays will meet at infinity.
Therefore, the focus of a plane mirror is at infinity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




