
Define quality factor.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: The students must remember that quality factor is a dimensionless quantity. So, it may be expressed as a ratio of two quantities having the same dimensions, or an approach may be taken by considering the fact that quality factor is something related to oscillations.
Complete step by step solution:
Definition:
In Physics, quality factor which is also named as Q-factor is a dimensionless parameter which describes the resonance behaviour of an under-damped harmonic oscillator. You might wonder what an under-damped oscillator is. So, in an oscillator, friction or damping slows down the motion of the system. In that case, the oscillations are categorized as damped oscillations. In a harmonic oscillator, we know that the force which acts is the restoring force, but if in addition to the restoring force, if we have frictional force (friction) acting on the harmonic oscillator, the oscillator is said to be damped, as the oscillations slow down. This is the case of a damped harmonic oscillator.
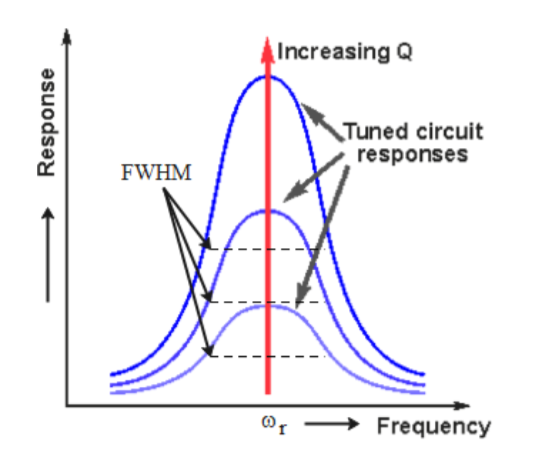
Now the quality factor of an oscillator which tells us how much damping is present in that oscillator. It is defined as follows:
$Q = \dfrac{{{\omega _r}}}{{\Delta \omega }}$
where Q is the quality factor of a given oscillator , ${\omega _r}$ signifies the resonant frequency of the oscillator while $\Delta \omega $ is known as the full-width at half-maximum.
Additional information:
A damping coefficient is a parameter which indicates whether a material will bounce back or return energy to a system.
Note: The students must not be confused about un-damped and under-damped oscillations. The un-damped oscillations means the absence of a damping force while the system is executing oscillations, whereas under-damped oscillations are those which have been described above.
Complete step by step solution:
Definition:
In Physics, quality factor which is also named as Q-factor is a dimensionless parameter which describes the resonance behaviour of an under-damped harmonic oscillator. You might wonder what an under-damped oscillator is. So, in an oscillator, friction or damping slows down the motion of the system. In that case, the oscillations are categorized as damped oscillations. In a harmonic oscillator, we know that the force which acts is the restoring force, but if in addition to the restoring force, if we have frictional force (friction) acting on the harmonic oscillator, the oscillator is said to be damped, as the oscillations slow down. This is the case of a damped harmonic oscillator.
Now the quality factor of an oscillator which tells us how much damping is present in that oscillator. It is defined as follows:
$Q = \dfrac{{{\omega _r}}}{{\Delta \omega }}$
where Q is the quality factor of a given oscillator , ${\omega _r}$ signifies the resonant frequency of the oscillator while $\Delta \omega $ is known as the full-width at half-maximum.

Additional information:
A damping coefficient is a parameter which indicates whether a material will bounce back or return energy to a system.
Note: The students must not be confused about un-damped and under-damped oscillations. The un-damped oscillations means the absence of a damping force while the system is executing oscillations, whereas under-damped oscillations are those which have been described above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




