
Define the negative of a vector.
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will, first of all, define a vector and its deviation by an example and then we will define the negative of a vector and use the example stated above to define the negative of that vector as stated in the above definition to get the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question, we will first of all define the positive of a vector or a vector itself. A vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] is given as
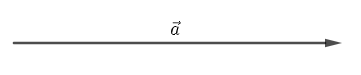
This is for example. This vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] points to the right-hand side means this is a vector in the right-hand side direction. Finally, let us define a negative of a vector. A negative vector is a vector that points in the direction opposite to the reference positive direction. A negative vector is that has the opposite direction to the reference of a positive direction. Like scalars, vectors can also be added and subtracted. Like the example taken above of vector, \[\overrightarrow{a}\] the negative of the vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] can be represented as \[-\overrightarrow{a}\] and will be drawn in the opposite direction to that of \[\overrightarrow{a}.\]
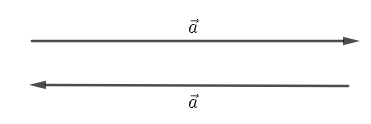
This is in the left direction.
Note: The magnitude of the vector never changes when the negative of the vector is taken. Also while calculating the negative of vector direction in accordance with the origin vector. It is not fixed in some specific direction in any case.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To solve this question, we will first of all define the positive of a vector or a vector itself. A vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] is given as
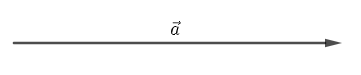
This is for example. This vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] points to the right-hand side means this is a vector in the right-hand side direction. Finally, let us define a negative of a vector. A negative vector is a vector that points in the direction opposite to the reference positive direction. A negative vector is that has the opposite direction to the reference of a positive direction. Like scalars, vectors can also be added and subtracted. Like the example taken above of vector, \[\overrightarrow{a}\] the negative of the vector \[\overrightarrow{a}\] can be represented as \[-\overrightarrow{a}\] and will be drawn in the opposite direction to that of \[\overrightarrow{a}.\]

This is in the left direction.
Note: The magnitude of the vector never changes when the negative of the vector is taken. Also while calculating the negative of vector direction in accordance with the origin vector. It is not fixed in some specific direction in any case.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




