
Define the Principal focus of a plane mirror.
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: We already know that the principal focus of a curved mirror is the point where the rays of light traveling parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to diverge from, after reflection. This definition is extended to the plane mirrors which are a limiting case of both concave and convex mirrors.
Complete step by step answer:
The principal focus of a mirror is the point where the rays of light incident on the mirror and traveling parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to meet.
In the case of concave mirrors, the principal focus is a real point at which the rays of light traveling parallel to the principal axis actually meet after reflection.
In the case of convex mirrors, however, the rays of light traveling parallel to the principal axis after reflection diverge away from the mirror. On the extension of the path of these light rays on the other side of the mirror, they seem to diverge from a single point which is known as the focus.
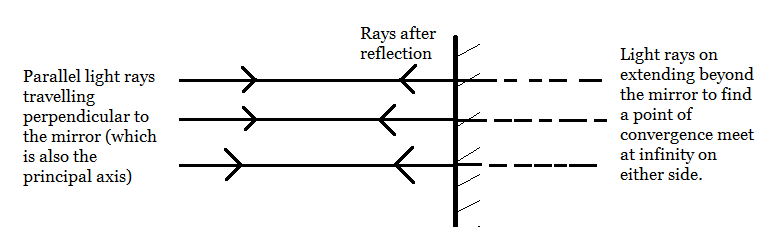
Now plane mirrors are an extreme case of either concave or convex mirrors. This means that in the case of plane mirrors, where the rays of light when traveling parallel to the principal axis reflect away, have the principal focus of infinite length. This is because these parallel rays are assumed to either meet at infinity on the same side of the mirror or are assumed to originate from the other side of the mirror where also it can be assumed to be originating from an infinite distance.
Thus, the principal focus of a plane mirror will lie at positive or negative infinity. Similarly, the center of curvature of the plane mirror will also lie at infinity on either side of the mirror.
Note: By the above findings we might also conclude that the principal focus of a plane mirror does not exist, since parallel rays of light never meet. Since a perfectly plane mirror is very hard to find and normal plane mirrors in use have some curvature however small they might be, we shall assume the position of the focus as being at a very large distance from the plane mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
The principal focus of a mirror is the point where the rays of light incident on the mirror and traveling parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to meet.
In the case of concave mirrors, the principal focus is a real point at which the rays of light traveling parallel to the principal axis actually meet after reflection.
In the case of convex mirrors, however, the rays of light traveling parallel to the principal axis after reflection diverge away from the mirror. On the extension of the path of these light rays on the other side of the mirror, they seem to diverge from a single point which is known as the focus.

Now plane mirrors are an extreme case of either concave or convex mirrors. This means that in the case of plane mirrors, where the rays of light when traveling parallel to the principal axis reflect away, have the principal focus of infinite length. This is because these parallel rays are assumed to either meet at infinity on the same side of the mirror or are assumed to originate from the other side of the mirror where also it can be assumed to be originating from an infinite distance.
Thus, the principal focus of a plane mirror will lie at positive or negative infinity. Similarly, the center of curvature of the plane mirror will also lie at infinity on either side of the mirror.
Note: By the above findings we might also conclude that the principal focus of a plane mirror does not exist, since parallel rays of light never meet. Since a perfectly plane mirror is very hard to find and normal plane mirrors in use have some curvature however small they might be, we shall assume the position of the focus as being at a very large distance from the plane mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




