
Define the scattering of light.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Scattering of light can be described as the phenomenon in which light rays deviate from their straight path when it hits an obstacle such as molecules of gas or dust, water vapors, etc. A day to day example of scattering of light is the Tyndall effect.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Scattering of light can be described as the phenomenon in which light rays deviate from their straight path when it hits an obstacle such as molecules of gas or dust, water vapors, etc. Scattering of light depends upon various factors like the size of the particles causing the scattering, the wavelength of the light being scattered, and the density of the medium containing the particles.
Scattering of light is shown in the diagram below
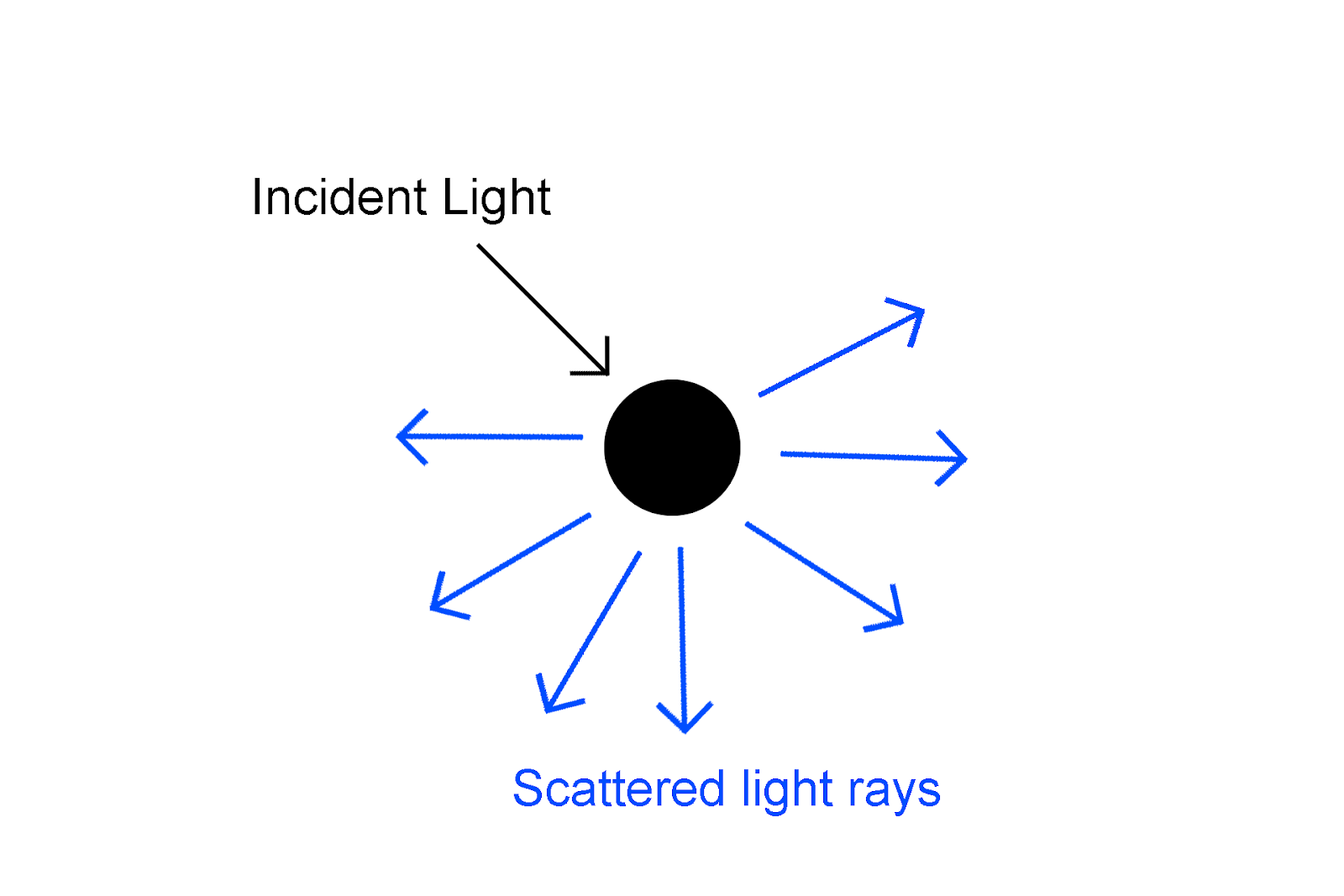
The light scattering phenomenon has given rise to many amazing phenomena, such as the Tyndall effect, and the color we see in the sky is due to light scattering. We can observe the basic Tyndall effect in our daily lives. Tyndall effect also referred to as the Tyndall phenomenon, is the scattering of a light ray in a medium containing tiny suspended particles, e.g. smoke or dust in a room, rendering a light beam visible entering a window. The effect is named after the British scientist John Tyndall of the 19th century, who first thoroughly studied it.
You can also see the scattering of light when the light from headlights passes through fog or mist on a cold day. Here the droplets of water scatter the light.
Note: In the solution above we discussed the scattering of light. This phenomenon is used in laboratories to determine the particle size of aerosols for quality control purposes. It is also used in radar sensing, medical ultrasound, computer-generated imagery, monitoring of polymerization reaction, etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Scattering of light can be described as the phenomenon in which light rays deviate from their straight path when it hits an obstacle such as molecules of gas or dust, water vapors, etc. Scattering of light depends upon various factors like the size of the particles causing the scattering, the wavelength of the light being scattered, and the density of the medium containing the particles.
Scattering of light is shown in the diagram below

The light scattering phenomenon has given rise to many amazing phenomena, such as the Tyndall effect, and the color we see in the sky is due to light scattering. We can observe the basic Tyndall effect in our daily lives. Tyndall effect also referred to as the Tyndall phenomenon, is the scattering of a light ray in a medium containing tiny suspended particles, e.g. smoke or dust in a room, rendering a light beam visible entering a window. The effect is named after the British scientist John Tyndall of the 19th century, who first thoroughly studied it.
You can also see the scattering of light when the light from headlights passes through fog or mist on a cold day. Here the droplets of water scatter the light.
Note: In the solution above we discussed the scattering of light. This phenomenon is used in laboratories to determine the particle size of aerosols for quality control purposes. It is also used in radar sensing, medical ultrasound, computer-generated imagery, monitoring of polymerization reaction, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




