
Define the term capsid.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Capsid is present in the virus. They are helpful in enclosing the genetic material of the virus. Not all the virus has capsid present in their structure. Different types of capsids can be seen in different types of the virus.
Complete answer:
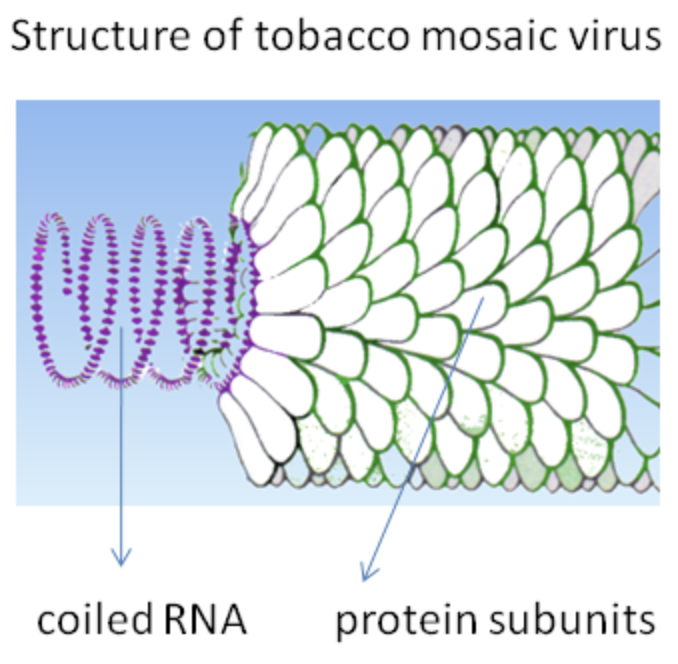
A virus particle usually consists of the capsid which is present to enclose their genetic material in it. It is a protective protein coat present around the DNA or RNA. The capsid is made from the proteins that are encoded by the viral genes present within their genome. The difference in the capsid shape can be seen as the basis of the classification of the virus. Helical capsids are made up of a single type of protein coat. The helix has a hollow entrance which makes it look-alike to the hollow tube. This type of capsid results in the formation of the rod-shaped virus. The tobacco mosaic virus has a helical capsid present. It causes diseases in various plant species.
The icosahedral capsid gives the virus a spherical shape. The protein subunits in it are arranged in a geometrical pattern. They are not truly spherical in nature. Adenovirus has an icosahedral type of capsid present in them. They are three dimensional in structure and have 20 equilateral triangles present which assembles together to form the capsid of this structure. The complex virus has neither helical or icosahedral capsids present in them. They have protein subunits arranged in a manner that they form the viral capsid. They have the presence of an icosahedral head capsid which has a tail and fibers attached to it. This can be seen in the E. coli bacteria.
Note: The capsid provides the protection to the genetic material of the virus. It is made up of the proteins units and subunits which lead to the formation of different types of capsid present in the viruses.
Complete answer:
A virus particle usually consists of the capsid which is present to enclose their genetic material in it. It is a protective protein coat present around the DNA or RNA. The capsid is made from the proteins that are encoded by the viral genes present within their genome. The difference in the capsid shape can be seen as the basis of the classification of the virus. Helical capsids are made up of a single type of protein coat. The helix has a hollow entrance which makes it look-alike to the hollow tube. This type of capsid results in the formation of the rod-shaped virus. The tobacco mosaic virus has a helical capsid present. It causes diseases in various plant species.

The icosahedral capsid gives the virus a spherical shape. The protein subunits in it are arranged in a geometrical pattern. They are not truly spherical in nature. Adenovirus has an icosahedral type of capsid present in them. They are three dimensional in structure and have 20 equilateral triangles present which assembles together to form the capsid of this structure. The complex virus has neither helical or icosahedral capsids present in them. They have protein subunits arranged in a manner that they form the viral capsid. They have the presence of an icosahedral head capsid which has a tail and fibers attached to it. This can be seen in the E. coli bacteria.
Note: The capsid provides the protection to the genetic material of the virus. It is made up of the proteins units and subunits which lead to the formation of different types of capsid present in the viruses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




