
Define Translatory motion.
Answer
611.1k+ views
- Hint: Translatory motion can be defined as a uniform motion where the different parts of the body do not change orientation with respect to each other.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Simply motion can be defined as the change of position concerning time. More broadly, motion can be defined as of three types :
Translatory motion
Rotational motion
Vibrational motion
There are many cases where the motion is described by one, two, or all of these in a single system.
Translational motion can be defined as the motion in which all points of a moving body move uniformly in the same line or direction. In due course of translation motion, the different points of an object do not change orientation to each other. Alternatively, in simple words, the body will not rotate or vibrate.
Examples: a ball moving in a parabolic path, a man walking in a straight road, etc
Translatory motion can be further classified into two types:
Curvilinear Motion
Rectilinear motion
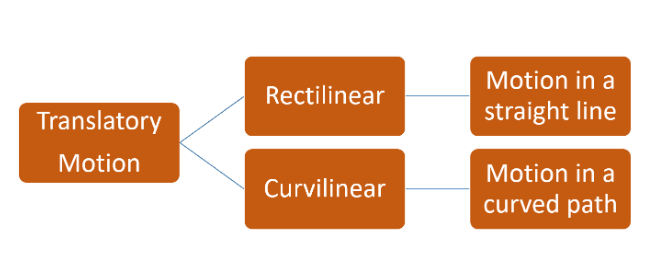
The motion is said to be curvilinear when the body is on a curved path. It is also motion in two-three dimensions. So pure translational motion does not always have to be in a straight line. This scenario is viable if an object moves in a curved path without changing its orientation.
Whereas the motion is said to be rectilinear when the body moves in a straight path. In this scenario, all the points of the moving system move parallel to each other, which ensures that there is no change in the orientation of the points that is no rotational motion.
Few more examples of translatory motion for better understanding:
Man walking
Car or bus moving.
Boat sailing in the sea.
Cat walking.
A stone falling straight towards the surface of the earth
A coin moving over a carrom board
Note: Student maximum times confuses translator motion with the motion in a straight line, but remember this is not necessary. Translation motion can be in a curved path also.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Simply motion can be defined as the change of position concerning time. More broadly, motion can be defined as of three types :
Translatory motion
Rotational motion
Vibrational motion
There are many cases where the motion is described by one, two, or all of these in a single system.
Translational motion can be defined as the motion in which all points of a moving body move uniformly in the same line or direction. In due course of translation motion, the different points of an object do not change orientation to each other. Alternatively, in simple words, the body will not rotate or vibrate.
Examples: a ball moving in a parabolic path, a man walking in a straight road, etc
Translatory motion can be further classified into two types:
Curvilinear Motion
Rectilinear motion

The motion is said to be curvilinear when the body is on a curved path. It is also motion in two-three dimensions. So pure translational motion does not always have to be in a straight line. This scenario is viable if an object moves in a curved path without changing its orientation.
Whereas the motion is said to be rectilinear when the body moves in a straight path. In this scenario, all the points of the moving system move parallel to each other, which ensures that there is no change in the orientation of the points that is no rotational motion.
Few more examples of translatory motion for better understanding:
Man walking
Car or bus moving.
Boat sailing in the sea.
Cat walking.
A stone falling straight towards the surface of the earth
A coin moving over a carrom board
Note: Student maximum times confuses translator motion with the motion in a straight line, but remember this is not necessary. Translation motion can be in a curved path also.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




