
What is the definition of inflection point? Or is it just not standardized like \[0 \in N\]?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: A point where the graph of a function has a tangent line and where the concavity change is called a point of inflection (i.e.)the points where the function change from being concave up to being concave down. These points are also called inflection points or flex.
Complete step-by-step solution:
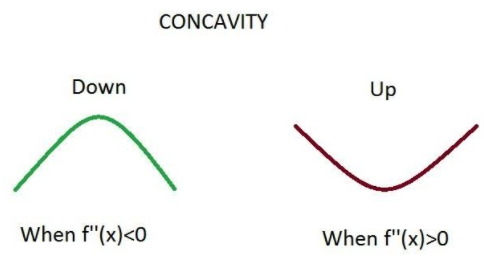
The sign of the second order derivative determines the concavity of the curve. If \[f''(x) > 0\forall x \in (a,b)\] then the graph of \[f\left( x \right)\] is concave upward in \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] .
Similarly if \[f''(x) < 0\forall x \in (a,b)\] then the graph of \[f\left( x \right)\] is concave downward in \[\left( {a,b} \right)\].
Point of inflection:
The point of inflection or inflection point is a point where the graph of a function has a tangent line and where the concavity of the function changes. It means that the function changes from down concave to up concave or vice versa. Those points are certainly not local maxima or minima. They are stationary points.
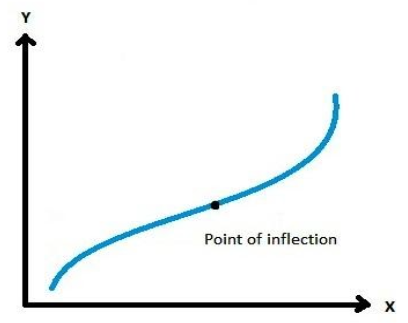
For finding the point of inflection of any function, compute the solutions of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 0\] or does not exist. Let the solution is x=a, if sign of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] changes about this point then it is called point of inflection.
Note:
> If at any point \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\]does not exist but sign of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\]changes about this point then it is also called point of inflection.
> If \[f'(x)\]does not change sign as x increases through c, then c is neither a point of Local maxima nor a point of local minima. In fact, such a point is called the point of inflection. So the condition for point of inflection is \[f''(x) = 0\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
The sign of the second order derivative determines the concavity of the curve. If \[f''(x) > 0\forall x \in (a,b)\] then the graph of \[f\left( x \right)\] is concave upward in \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] .
Similarly if \[f''(x) < 0\forall x \in (a,b)\] then the graph of \[f\left( x \right)\] is concave downward in \[\left( {a,b} \right)\].

Point of inflection:
The point of inflection or inflection point is a point where the graph of a function has a tangent line and where the concavity of the function changes. It means that the function changes from down concave to up concave or vice versa. Those points are certainly not local maxima or minima. They are stationary points.

For finding the point of inflection of any function, compute the solutions of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 0\] or does not exist. Let the solution is x=a, if sign of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] changes about this point then it is called point of inflection.
Note:
> If at any point \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\]does not exist but sign of \[\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\]changes about this point then it is also called point of inflection.
> If \[f'(x)\]does not change sign as x increases through c, then c is neither a point of Local maxima nor a point of local minima. In fact, such a point is called the point of inflection. So the condition for point of inflection is \[f''(x) = 0\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




