
Demonstrate the phenomenon of transpiration
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Transpiration is a phenomenon that helps in passive absorption of water. It is absent from desert plants or plants living in xerophytic conditions. Transpiration influences climatic factors such as precipitation over a region.
Complete answer:
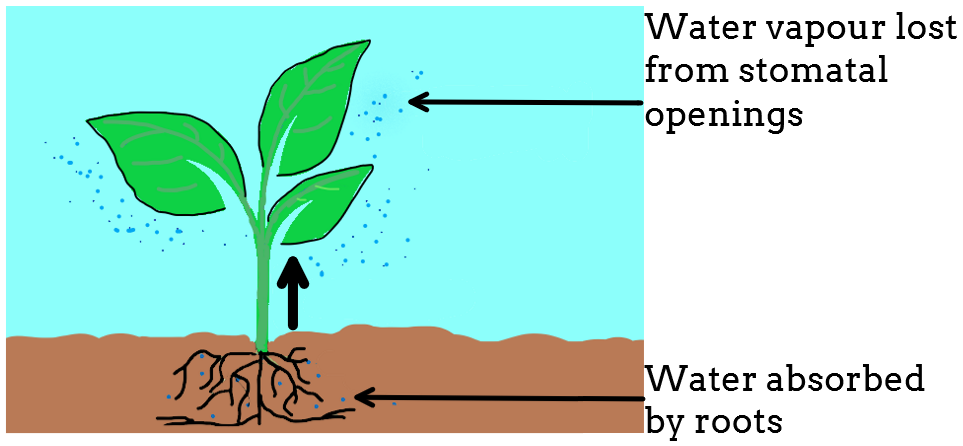
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost in the form of water vapor from the leaf surfaces through the stomatal opening. Loss of water generated a pull throughout the xylem vessel which helps in water absorption. Transpiration rate is measured by a device known as the potometer.
Transpiration is mainly of three different types:
-Cuticular transpiration: Transpiration occurs through the cuticle. It contributes 3-10% to the total transpiration is trees, but in herbs and ferns, cuticular transpiration accounts for almost 50% of the total transpiration.
-Stomatal transpiration: Stomatal transpiration is how maximum water loss takes place. It accounts for 50-97% of total transpiration. It occurs only through leaves.
-Lenticular Transpiration: Lenticels present on the woody stems may also take part in transpiration. They contribute a very small percentage to transpiration which is around 0.1 to 1%.
-Transpiration helps in the cooling of plants when temperatures are too high.
-The rate of transpiration is dependent on several factors like humidity, wind speed, temperature, etc.
-Transpiration is absent in plants surviving under xerophytic conditions. Leaves of these plants are converted into spines to prevent water loss by transpiration.
Note: It should be remembered that even though leaves are reduced to spines in xerophytes, still transpiration is observed in these xerophytes. These tend to open their stomata only at night time so that too much water is not lost by excessive evaporation during day time. Several adaptations are shown by xerophytic plants, such as low stomatal density, thick cuticle, reduction of leaves to spine, etc.
Complete answer:
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost in the form of water vapor from the leaf surfaces through the stomatal opening. Loss of water generated a pull throughout the xylem vessel which helps in water absorption. Transpiration rate is measured by a device known as the potometer.
Transpiration is mainly of three different types:
-Cuticular transpiration: Transpiration occurs through the cuticle. It contributes 3-10% to the total transpiration is trees, but in herbs and ferns, cuticular transpiration accounts for almost 50% of the total transpiration.
-Stomatal transpiration: Stomatal transpiration is how maximum water loss takes place. It accounts for 50-97% of total transpiration. It occurs only through leaves.
-Lenticular Transpiration: Lenticels present on the woody stems may also take part in transpiration. They contribute a very small percentage to transpiration which is around 0.1 to 1%.
-Transpiration helps in the cooling of plants when temperatures are too high.
-The rate of transpiration is dependent on several factors like humidity, wind speed, temperature, etc.
-Transpiration is absent in plants surviving under xerophytic conditions. Leaves of these plants are converted into spines to prevent water loss by transpiration.
Note: It should be remembered that even though leaves are reduced to spines in xerophytes, still transpiration is observed in these xerophytes. These tend to open their stomata only at night time so that too much water is not lost by excessive evaporation during day time. Several adaptations are shown by xerophytic plants, such as low stomatal density, thick cuticle, reduction of leaves to spine, etc.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




