
What is the depletion region in the pn junction?
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: We know that there are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a region of a certain width develops between them. The word depletion meant reduction in something.
Complete answer:
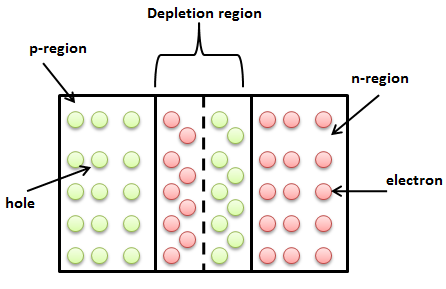
We know that there are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a depletion region develops between them. The word depletion meant reduction in something. We know that in p-type semiconductor, holes are majority charge carriers and in n-type semiconductor, electrons are majority charge carriers. The depletion region or pn junction separates p-region and n-region in the semiconductor device.
We will now discuss how the depletion region forms? Since in n-type semiconductor, electrons are charged carriers and are free to move. We know that the electrons move from high concentrated region (n-region) to low concentrated region (p-region). This is primarily due to electrostatic force which deflects electrons from n-region to p-region. In the same manner, the holes from the p-region are moved towards the n-region. We know that in the p-region, there is a deficiency of electrons. Therefore, the atoms in the p-region gain electrons and become negatively charged. Similarly, the atoms in the n-region gain extra holes and attain positive charge. When the charge transfer attains threshold, it prevents transfer of extra electrons to the p-region due to net repulsion from the p-region.
Note:
The depletion regions break down when we connect the semiconductor device in a forward bias when the voltage increases beyond the threshold value. When we connect the semiconductor device in a reverse bias, the width of the depletion regions gets wider until it reaches its threshold value. After a certain value of applied voltage, this depletion region also gets a break and we can see the sharp rise in the current.
Complete answer:
We know that there are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a depletion region develops between them. The word depletion meant reduction in something. We know that in p-type semiconductor, holes are majority charge carriers and in n-type semiconductor, electrons are majority charge carriers. The depletion region or pn junction separates p-region and n-region in the semiconductor device.
We will now discuss how the depletion region forms? Since in n-type semiconductor, electrons are charged carriers and are free to move. We know that the electrons move from high concentrated region (n-region) to low concentrated region (p-region). This is primarily due to electrostatic force which deflects electrons from n-region to p-region. In the same manner, the holes from the p-region are moved towards the n-region. We know that in the p-region, there is a deficiency of electrons. Therefore, the atoms in the p-region gain electrons and become negatively charged. Similarly, the atoms in the n-region gain extra holes and attain positive charge. When the charge transfer attains threshold, it prevents transfer of extra electrons to the p-region due to net repulsion from the p-region.

Note:
The depletion regions break down when we connect the semiconductor device in a forward bias when the voltage increases beyond the threshold value. When we connect the semiconductor device in a reverse bias, the width of the depletion regions gets wider until it reaches its threshold value. After a certain value of applied voltage, this depletion region also gets a break and we can see the sharp rise in the current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




