
What is the derivative graph of a parabola?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: In this problem we need to find the derivative graph of a parabola. For this we will first assume the standard equation of the parabola which is given by $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ where $a$, $b$, $c$ are the constants. Now we will differentiate the above equation with respect to the variable $x$. By using the differentiation formula, we will simplify the obtained equation to get the required result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the equation of the parabola will be $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$.
Differentiating the above equation with respect to $x$, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$
Applying the differentiation for each term individually, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( a{{x}^{2}} \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( bx \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
Taking out the constants from differentiation which are in multiplication with the variables in the above equation, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)+b\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
From the differentiation formula $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}$ we can write the value of $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)$ as $2x$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
We have the value $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)=1$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\left( 1 \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
The value $c$ which is in the above equation is a constant. We know that differentiation value of a constant is equals to zero. By using this value, we can write the above equation as
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\left( 1 \right)+0$
Simplifying the above equation by using the basic mathematical operations, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=2ax+b$
The equation $2ax+b$ represents the equation of the line. We can observe this in the below graph also
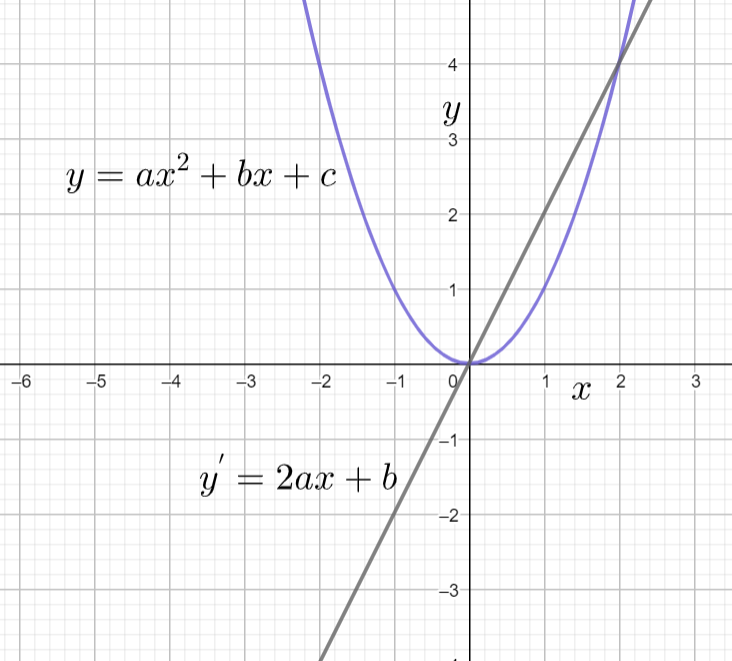
Hence the derivative graph of the parabola is Straight Line.
Note: In this problem we have assumed the equation of the parabola as $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ instead of $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$ even though the both the equations represent the parabola. Because the equation $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ has an extra advantage to calculate the differentiation value easily over the equation $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the equation of the parabola will be $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$.
Differentiating the above equation with respect to $x$, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$
Applying the differentiation for each term individually, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( a{{x}^{2}} \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( bx \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
Taking out the constants from differentiation which are in multiplication with the variables in the above equation, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)+b\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
From the differentiation formula $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}$ we can write the value of $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)$ as $2x$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
We have the value $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)=1$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\left( 1 \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( c \right)$
The value $c$ which is in the above equation is a constant. We know that differentiation value of a constant is equals to zero. By using this value, we can write the above equation as
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=a\left( 2x \right)+b\left( 1 \right)+0$
Simplifying the above equation by using the basic mathematical operations, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=2ax+b$
The equation $2ax+b$ represents the equation of the line. We can observe this in the below graph also

Hence the derivative graph of the parabola is Straight Line.
Note: In this problem we have assumed the equation of the parabola as $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ instead of $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$ even though the both the equations represent the parabola. Because the equation $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ has an extra advantage to calculate the differentiation value easily over the equation $x=a{{y}^{2}}+by+c$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




