
Derive an expression for mechanical force per unit area of surface charge density.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: The quantity of charge contained per unit area is called surface charge density. All charged conductors will experience some mechanical force. Elements having a surface charge density will always experience a mechanical force outwards. Here we have to derive an expression for the mechanical force.
Complete step by step answer:
Small elements of the conductor will experience a mechanical force normally outwards. Let us consider the small element $dS$ as shown below,
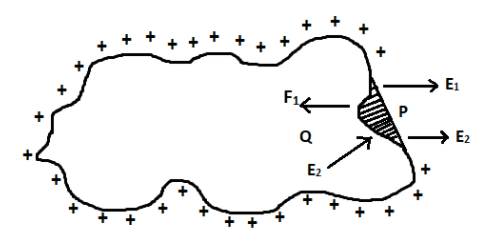
Let $\sigma $ be the surface charge density of the conductor. Then the charge carried by the small element $dS$ be $dq$.
Then we can write,
$dq = \sigma dS$ -------$(1)$
Let us consider a point $P$ outside the small element as shown in the figure.
At this point $P$, the electrical intensity can be written as,
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$ -------$(2)$
where ${\varepsilon _0}$ stands for the permittivity of free space and $k$ stands for the dielectric constant.
The electrical intensity is directed normally outwards.
The electrical intensity $E$ can be resolved into two components, ${E_1}$ and ${E_2}$.
$\overrightarrow {{E_1}} $ is the component of electrical intensity due to the small charge $dq$present in the element.
${\vec E_2}$ is the component due to the rest of the charges present on the surface.
Hence the total electrical intensity at the point $P$ can be written as,
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
Substituting this value in equation $(2)$
${E_1} + {E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$ --------$(3)$
Let us now consider the point $Q$. At this point, the components of electrical intensity are in opposite direction. Inside the charged conductor the total charge is zero.
i.e.
${E_1} - {E_2} = 0$
$\therefore {E_1} = {E_2}$
Substituting ${E_1} = {E_2}$ in equation $(3)$
We get
${E_2} + {E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
This can be written as,
$2{E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
From this, we can write ${E_2}$ as,
${E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
We know that the electrical intensity due to the rest of the charges in the conductor is ${E_2}$. The element $dS$ of the conductor will experience a repulsive force due to this component.
The repulsive force experienced by the rest of the conductor due to the charge $dq$ in the small element $dS$ is given by,
$F = {E_2}dq$
We know that ${E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
and $dq = \sigma dS$
Substituting these values in the equation for force,
$F = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}.\sigma .ds = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}dS$
From this equation, we can write
$\dfrac{F}{{dS}} = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
The force per unit area can be written as, $\dfrac{F}{{dS}} = f$
Thus the above equation will become,
$f = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
This is the mechanical force per unit area of a conductor due to a surface charge density.
Note: The S.I unit for the mechanical force per unit area is given by $N/{m^2}$. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract. In a charge-carrying conductor, the charges are all similar. Hence when we consider a small element the rest of the conductor will experience the mechanical force due to the repulsion of like charges.
Complete step by step answer:
Small elements of the conductor will experience a mechanical force normally outwards. Let us consider the small element $dS$ as shown below,

Let $\sigma $ be the surface charge density of the conductor. Then the charge carried by the small element $dS$ be $dq$.
Then we can write,
$dq = \sigma dS$ -------$(1)$
Let us consider a point $P$ outside the small element as shown in the figure.
At this point $P$, the electrical intensity can be written as,
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$ -------$(2)$
where ${\varepsilon _0}$ stands for the permittivity of free space and $k$ stands for the dielectric constant.
The electrical intensity is directed normally outwards.
The electrical intensity $E$ can be resolved into two components, ${E_1}$ and ${E_2}$.
$\overrightarrow {{E_1}} $ is the component of electrical intensity due to the small charge $dq$present in the element.
${\vec E_2}$ is the component due to the rest of the charges present on the surface.
Hence the total electrical intensity at the point $P$ can be written as,
$E = {E_1} + {E_2}$
Substituting this value in equation $(2)$
${E_1} + {E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$ --------$(3)$
Let us now consider the point $Q$. At this point, the components of electrical intensity are in opposite direction. Inside the charged conductor the total charge is zero.
i.e.
${E_1} - {E_2} = 0$
$\therefore {E_1} = {E_2}$
Substituting ${E_1} = {E_2}$ in equation $(3)$
We get
${E_2} + {E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
This can be written as,
$2{E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
From this, we can write ${E_2}$ as,
${E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
We know that the electrical intensity due to the rest of the charges in the conductor is ${E_2}$. The element $dS$ of the conductor will experience a repulsive force due to this component.
The repulsive force experienced by the rest of the conductor due to the charge $dq$ in the small element $dS$ is given by,
$F = {E_2}dq$
We know that ${E_2} = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
and $dq = \sigma dS$
Substituting these values in the equation for force,
$F = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}.\sigma .ds = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}dS$
From this equation, we can write
$\dfrac{F}{{dS}} = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
The force per unit area can be written as, $\dfrac{F}{{dS}} = f$
Thus the above equation will become,
$f = \dfrac{{{\sigma ^2}}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}k}}$
This is the mechanical force per unit area of a conductor due to a surface charge density.
Note: The S.I unit for the mechanical force per unit area is given by $N/{m^2}$. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract. In a charge-carrying conductor, the charges are all similar. Hence when we consider a small element the rest of the conductor will experience the mechanical force due to the repulsion of like charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




