
Derive Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Answer
519.9k+ views
Hint: Einstein’s photoelectric equation can be derived using the fact that it is based on Planck's quantum theory. Equate the expression for the energy of the incident photon and maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photon and work function of the metal to get the required expression of Einstein’s photoelectric.
Complete step-by-step answer:
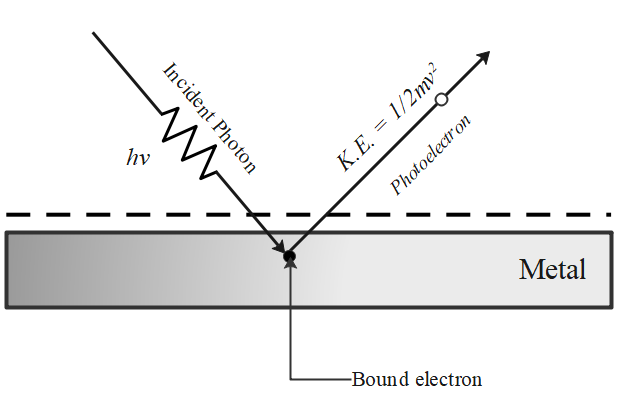
The phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface, when electromagnetic radiations of sufficiently high frequency are incident on it, is called the photoelectric effect.
Einstein explained the photoelectric effect based on Planck's quantum theory according to which light radiation travels in the form of discrete photons. The energy of each photon is $hv$, where $h$ is Planck's constant and $v$ is the frequency of light.
The main points of Einstein’s theory of the photoelectric effect are:
The interaction between two particles results in photoelectric emission– one a photon of incident radiation and the other an electron of photosensitive metal.
The free electrons are bound within the metal due to restraining forces on the surface. The minimum energy required to liberate an electron from the metal surface is called the work function ${W_ \circ }$ of the metal.
Each photon interacts with one electron. The energy $hv$of the incident photon is used up in two parts:
A part of the energy of the photon is used in liberating the electron from the metal surface, which is equal to the work function ${W_ \circ }$ of the metal, and
The remaining energy of the photon is used in impairing kinetic energy to the ejected electron.
Very few (<1%) photons, whose energies are greater than ${W_ \circ }$, capable of ejecting the photons.
By law of the conservation of energy,
Energy of the incident photon = Maximum K.E. of photon + Work function
$\eqalign{
& hv = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 + {W_ \circ } \cr
& \therefore {K_{\max }} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 = hv - {W_ \circ } \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right) \cr} $
If the incident photon is threshold frequency ${v_ \circ }$, then its energy $h{v_ \circ }$is just sufficient to free the electron from the metal surface and does not give it any kinetic energy. So $h{v_ \circ } = {W_ \circ }$. Hence
${K_{\max }} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 = hv - h{v_ \circ } = h\left( {v - {v_ \circ }} \right) \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Equations (1) and (2) are called Einstein’s photoelectric equations.
Note: Photoelectric emission is the result of an elastic collision between a photon and an electron. Thus the absorption of energy from a photon by a free electron inside the metal is a single event that involves the transfer of energy in one lump instead of the continuous absorption of energy as in the wave theory of light.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface, when electromagnetic radiations of sufficiently high frequency are incident on it, is called the photoelectric effect.
Einstein explained the photoelectric effect based on Planck's quantum theory according to which light radiation travels in the form of discrete photons. The energy of each photon is $hv$, where $h$ is Planck's constant and $v$ is the frequency of light.
The main points of Einstein’s theory of the photoelectric effect are:
The interaction between two particles results in photoelectric emission– one a photon of incident radiation and the other an electron of photosensitive metal.
The free electrons are bound within the metal due to restraining forces on the surface. The minimum energy required to liberate an electron from the metal surface is called the work function ${W_ \circ }$ of the metal.
Each photon interacts with one electron. The energy $hv$of the incident photon is used up in two parts:
A part of the energy of the photon is used in liberating the electron from the metal surface, which is equal to the work function ${W_ \circ }$ of the metal, and
The remaining energy of the photon is used in impairing kinetic energy to the ejected electron.

Very few (<1%) photons, whose energies are greater than ${W_ \circ }$, capable of ejecting the photons.
By law of the conservation of energy,
Energy of the incident photon = Maximum K.E. of photon + Work function
$\eqalign{
& hv = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 + {W_ \circ } \cr
& \therefore {K_{\max }} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 = hv - {W_ \circ } \cdots \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right) \cr} $
If the incident photon is threshold frequency ${v_ \circ }$, then its energy $h{v_ \circ }$is just sufficient to free the electron from the metal surface and does not give it any kinetic energy. So $h{v_ \circ } = {W_ \circ }$. Hence
${K_{\max }} = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2 = hv - h{v_ \circ } = h\left( {v - {v_ \circ }} \right) \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Equations (1) and (2) are called Einstein’s photoelectric equations.
Note: Photoelectric emission is the result of an elastic collision between a photon and an electron. Thus the absorption of energy from a photon by a free electron inside the metal is a single event that involves the transfer of energy in one lump instead of the continuous absorption of energy as in the wave theory of light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




