
Derive Einstein's photoelectric equation. Explain the photoelectric effect with the help of this equation.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which the electrically charged particles are ejected from the material or within the material whenever it absorbs electromagnetic radiation. The effect is sometimes described as the ejection of electrons from a metal plate when light is incident on it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
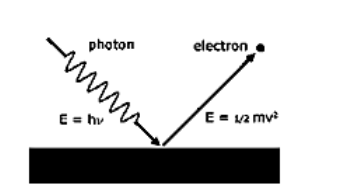
First of all let us discuss the photoelectric effect in detail. The photoelectric effect is defined as the ejection of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, for example light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are known as photoelectrons. The photoelectric effect happens when light falls on a metal. Often electrons are being emitted. Light at any frequency will result in electrons to be emitted. Einstein’s photoelectric equation is given as,
The energy of the incident photon is equal to the sum of the maximum kinetic energy of an electron and the work function.
This is based on energy conservation,
$h\nu =\dfrac{1}{2}m{{V}_{\max }}^{2}+{{W}_{0}}$
Where ${{W}_{0}}$ the work function.
${{W}_{0}}=\dfrac{h{{\nu }_{0}}}{\gamma }$
$\gamma $Is the threshold frequency.
Therefore the maximum kinetic energy is,
$\begin{align}
& {{K}_{\max }}=h\nu -h{{\nu }_{0}} \\
& =h\left( \nu -{{\nu }_{0}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
As the intensity increases, the number of photons striking the metal surface at a unit time increases. So the number of ejected electrons increases. If frequency of incident radiation becomes less than the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of photoelectrons will be negative. This is no physical meaning for this. The maximum kinetic energy increases linearly with frequency.
Note: The more intense the light falls, the more kinetic energy the emitted electrons will have. Study of the photoelectric effect led to necessary steps in understanding the quantum nature of light and electrons and influenced the formation of the concept of dual nature of a wave. The photoelectric effect is also commonly used to investigate electron energy levels in matter.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us discuss the photoelectric effect in detail. The photoelectric effect is defined as the ejection of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, for example light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are known as photoelectrons. The photoelectric effect happens when light falls on a metal. Often electrons are being emitted. Light at any frequency will result in electrons to be emitted. Einstein’s photoelectric equation is given as,
The energy of the incident photon is equal to the sum of the maximum kinetic energy of an electron and the work function.
This is based on energy conservation,
$h\nu =\dfrac{1}{2}m{{V}_{\max }}^{2}+{{W}_{0}}$
Where ${{W}_{0}}$ the work function.
${{W}_{0}}=\dfrac{h{{\nu }_{0}}}{\gamma }$
$\gamma $Is the threshold frequency.
Therefore the maximum kinetic energy is,
$\begin{align}
& {{K}_{\max }}=h\nu -h{{\nu }_{0}} \\
& =h\left( \nu -{{\nu }_{0}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
As the intensity increases, the number of photons striking the metal surface at a unit time increases. So the number of ejected electrons increases. If frequency of incident radiation becomes less than the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of photoelectrons will be negative. This is no physical meaning for this. The maximum kinetic energy increases linearly with frequency.

Note: The more intense the light falls, the more kinetic energy the emitted electrons will have. Study of the photoelectric effect led to necessary steps in understanding the quantum nature of light and electrons and influenced the formation of the concept of dual nature of a wave. The photoelectric effect is also commonly used to investigate electron energy levels in matter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




