
Derive expression for amplitude modulated wave? What is meant by side band frequency in carrier waves?
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Modulation is the process of mixing a carrier wave with an input signal which contains information. In amplitude modulation, the input signal mixes and changes the amplitude of the carrier wave. The new wave also gives rise to a number of waves of different frequencies.
Complete answer:
The process of mixing an input signal with a carrier signal is called modulation. It changes the shape of the carrier signal to encode information that needs to be carried through the wave.
When an input wave is mixed with the carrier wave such that the amplitude of the final wave changes it is called an amplitude modulated wave. It is used to carry signals.
Let the amplitude modulated wave be-
$m(t)={{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)$ - (1)
Here, ${{A}_{m}}$is the amplitude of input signal
${{f}_{m}}$is the frequency of input signal
$t$is time taken
The carrier wave is represented as-
$c(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)$ - (2)
Here${{A}_{c}}$is the amplitude of carrier wave
${{f}_{c}}$is the frequency of the carrier wave
Form eq (1) and eq (2), the amplitude modulated wave can be represented as-
$a(t)=({{A}_{c}}+{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t))\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)~~~~$ - (3)
Therefore, the equation of an amplitude modulated wave is-$a(t)=({{A}_{c}}+{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t))\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)~~~$
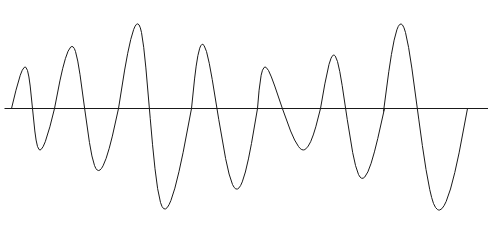
Carrier wave
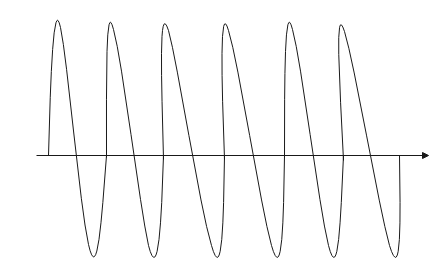
Input wave
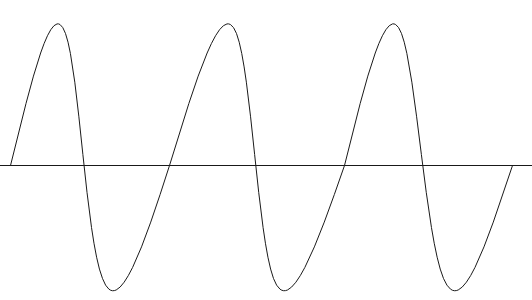
Amplitude modulated wave
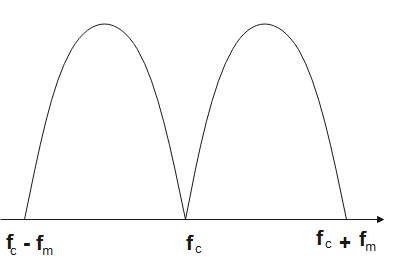
Due to the modulation process, the band of frequencies generated that are higher than or lower than the carrier frequencies are called sideband frequencies.
The frequencies that are above that carrier frequency are called upper sideband (USB) and those that are below the carrier frequencies are called lower sideband (LSB). $\begin{align}
& a(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\,+\dfrac{2}{2}{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t) \\
& a(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\,+\dfrac{{{A}_{m}}}{2}\cos (2\pi t[{{f}_{m}}-{{f}_{c}}])+\cos (2\pi t[{{f}_{m}}+{{f}_{c}}]) \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Note:
The other ways of modulating a carrier wave are-frequency modulation and phase modulation. In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier wave is changed while in phase modulation, the phase changes. The carrier wave contains the energy required to take the information in the input signal from one place to the other.
Complete answer:
The process of mixing an input signal with a carrier signal is called modulation. It changes the shape of the carrier signal to encode information that needs to be carried through the wave.
When an input wave is mixed with the carrier wave such that the amplitude of the final wave changes it is called an amplitude modulated wave. It is used to carry signals.
Let the amplitude modulated wave be-
$m(t)={{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)$ - (1)
Here, ${{A}_{m}}$is the amplitude of input signal
${{f}_{m}}$is the frequency of input signal
$t$is time taken
The carrier wave is represented as-
$c(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)$ - (2)
Here${{A}_{c}}$is the amplitude of carrier wave
${{f}_{c}}$is the frequency of the carrier wave
Form eq (1) and eq (2), the amplitude modulated wave can be represented as-
$a(t)=({{A}_{c}}+{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t))\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)~~~~$ - (3)
Therefore, the equation of an amplitude modulated wave is-$a(t)=({{A}_{c}}+{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t))\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)~~~$
Carrier wave

Input wave

Amplitude modulated wave

Due to the modulation process, the band of frequencies generated that are higher than or lower than the carrier frequencies are called sideband frequencies.
The frequencies that are above that carrier frequency are called upper sideband (USB) and those that are below the carrier frequencies are called lower sideband (LSB). $\begin{align}
& a(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\,+\dfrac{2}{2}{{A}_{m}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t) \\
& a(t)={{A}_{c}}\cos (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\,+\dfrac{{{A}_{m}}}{2}\cos (2\pi t[{{f}_{m}}-{{f}_{c}}])+\cos (2\pi t[{{f}_{m}}+{{f}_{c}}]) \\
& \\
\end{align}$

Note:
The other ways of modulating a carrier wave are-frequency modulation and phase modulation. In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier wave is changed while in phase modulation, the phase changes. The carrier wave contains the energy required to take the information in the input signal from one place to the other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




