
Derive the following expression for the refraction at concave spherical surface:
$ \dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}. $
Answer
522.2k+ views
Hint
A spherical mirror is a part of a sphere with a reflecting surface. If the inner surface is the reflective surface then the mirror is called a concave mirror and if the outer surface is the reflecting surface then the mirror is called a convex mirror. Here we have a concave reflecting surface for which we have to derive the given expression.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider a concave mirror as shown in the diagram below,
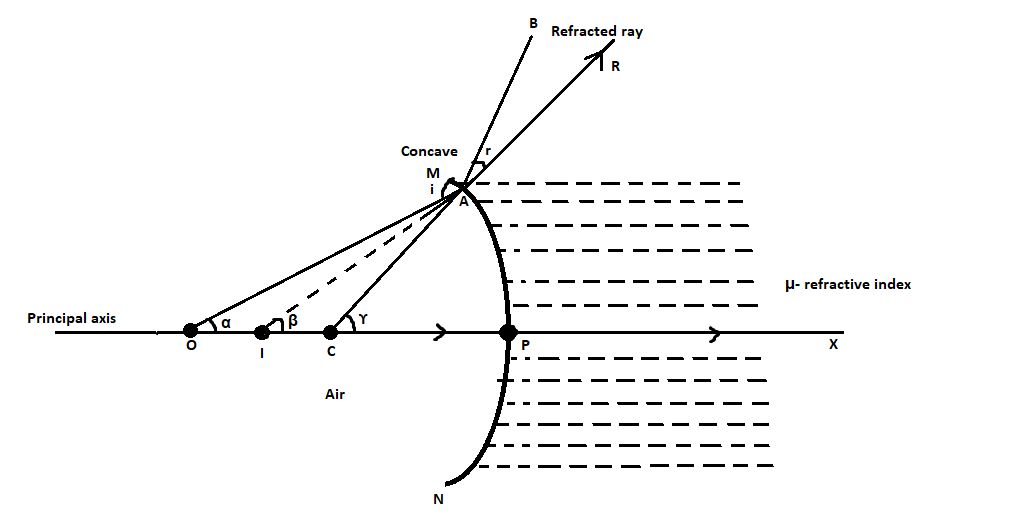
The concave mirror is represented by $ MPN $ . The refractive index of the medium of the spherical surface is given by $ \mu $ . We consider $ P $ as the pole of the mirror, $ O $ as the centre of curvature, and $ PC $ represents the principal axis of the refractive spherical surface. We consider a point object at $ O $ . An incident ray travels through $ C $ and it is normal to the spherical surface. It will not undergo any refraction hence it will travel in a straight line along $ PX $ . Another ray that we consider is $ OA $ . It will refract at the point $ A $ bending towards the normal. At a point $ i $ we will get a virtual image.
Let us consider the ray angles with the principal axis to be $ \alpha,\beta $ , and $ \gamma $ respectively.
According to Snell’s law, we can write the refractive index as
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} $
Where $ i $ is the angle of incidence and $ r $ is the angle of refraction.
Here we have very small $ i $ and $ r $ , hence we can write,
$\Rightarrow \sin i = i $ And $ \sin r = r $ in equation
We get,
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{i}{r} $
From this we get,
$\Rightarrow i = \mu r $
By using the exterior angle theorem, from $ \Delta AOC $ we get,
$\Rightarrow \gamma = i + \alpha $
From this we get
$\Rightarrow i = \gamma - \alpha $
Now, by using exterior angle theorem in $ \Delta IAC $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \gamma = \beta + r $
From this we get,
$\Rightarrow r = \gamma - \beta $
Substituting these values of $ i $ and $ r $ in equation we get,
$\Rightarrow \left( {\gamma - \alpha } \right) = \mu \left( {\gamma - \beta } \right) $
For a spherical surface, we can write the angle as
$\Rightarrow angle = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
We can write
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{PA}}{{OP}} $
And
$\Rightarrow \beta = \dfrac{{PA}}{{IP}} $
Also
$\Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{{PA}}{{CP}} $
Substituting these values of $ \alpha ,\beta $ and $ \gamma $ in , we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{PA}}{{PC}} - \dfrac{{PA}}{{PO}} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{{PA}}{{PC}} - \dfrac{{PA}}{{PI}}} \right) $
Taking the common terms outside we get,
$\Rightarrow PA\left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}}} \right) = \mu PA\left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow PA $ gets cancelled as it is common on both sides. Now we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PI}}} \right) $
Now we have to apply the sign convention.
$\Rightarrow PC = - R $ (where $ R $ is the radius of curvature)
$\Rightarrow PI = - v $ (Where $ v $ is the distance of the image from the pole of the mirror)
$\Rightarrow PO = - u $ (Where $ u $ is the distance of the object from the pole of the mirror)
Putting these values in equation
We get,
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - R}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - u}}} \right) = \mu \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - R}} + \dfrac{1}{v}} \right) $
Opening the brackets on LHS
$\Rightarrow\dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{v}} \right)$
Opening the brackets on RHS
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{\mu }{R} + \dfrac{\mu }{v} $
Rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{\mu }{R} = \dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
We can write this expression as,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R} = \dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
Hence we got the required expression for the concave refractive surface.
Note
According to the Cartesian sign convention,
-All distances as measured from the pole of the mirror.
-The distances that are measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive.
-The distances that are measured opposite to the direction of incident light is considered as negative.
-The height measured upward the principal axis is measured as positive and the height measured downward is measured negative.
A spherical mirror is a part of a sphere with a reflecting surface. If the inner surface is the reflective surface then the mirror is called a concave mirror and if the outer surface is the reflecting surface then the mirror is called a convex mirror. Here we have a concave reflecting surface for which we have to derive the given expression.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider a concave mirror as shown in the diagram below,

The concave mirror is represented by $ MPN $ . The refractive index of the medium of the spherical surface is given by $ \mu $ . We consider $ P $ as the pole of the mirror, $ O $ as the centre of curvature, and $ PC $ represents the principal axis of the refractive spherical surface. We consider a point object at $ O $ . An incident ray travels through $ C $ and it is normal to the spherical surface. It will not undergo any refraction hence it will travel in a straight line along $ PX $ . Another ray that we consider is $ OA $ . It will refract at the point $ A $ bending towards the normal. At a point $ i $ we will get a virtual image.
Let us consider the ray angles with the principal axis to be $ \alpha,\beta $ , and $ \gamma $ respectively.
According to Snell’s law, we can write the refractive index as
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} $
Where $ i $ is the angle of incidence and $ r $ is the angle of refraction.
Here we have very small $ i $ and $ r $ , hence we can write,
$\Rightarrow \sin i = i $ And $ \sin r = r $ in equation
We get,
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{i}{r} $
From this we get,
$\Rightarrow i = \mu r $
By using the exterior angle theorem, from $ \Delta AOC $ we get,
$\Rightarrow \gamma = i + \alpha $
From this we get
$\Rightarrow i = \gamma - \alpha $
Now, by using exterior angle theorem in $ \Delta IAC $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \gamma = \beta + r $
From this we get,
$\Rightarrow r = \gamma - \beta $
Substituting these values of $ i $ and $ r $ in equation we get,
$\Rightarrow \left( {\gamma - \alpha } \right) = \mu \left( {\gamma - \beta } \right) $
For a spherical surface, we can write the angle as
$\Rightarrow angle = \dfrac{{arc}}{{radius}} $
We can write
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{PA}}{{OP}} $
And
$\Rightarrow \beta = \dfrac{{PA}}{{IP}} $
Also
$\Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{{PA}}{{CP}} $
Substituting these values of $ \alpha ,\beta $ and $ \gamma $ in , we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{PA}}{{PC}} - \dfrac{{PA}}{{PO}} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{{PA}}{{PC}} - \dfrac{{PA}}{{PI}}} \right) $
Taking the common terms outside we get,
$\Rightarrow PA\left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}}} \right) = \mu PA\left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow PA $ gets cancelled as it is common on both sides. Now we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PO}} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{1}{{PC}} - \dfrac{1}{{PI}}} \right) $
Now we have to apply the sign convention.
$\Rightarrow PC = - R $ (where $ R $ is the radius of curvature)
$\Rightarrow PI = - v $ (Where $ v $ is the distance of the image from the pole of the mirror)
$\Rightarrow PO = - u $ (Where $ u $ is the distance of the object from the pole of the mirror)
Putting these values in equation
We get,
$\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - R}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - u}}} \right) = \mu \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - R}} + \dfrac{1}{v}} \right) $
Opening the brackets on LHS
$\Rightarrow\dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \mu \left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{v}} \right)$
Opening the brackets on RHS
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{\mu }{R} + \dfrac{\mu }{v} $
Rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{R} + \dfrac{\mu }{R} = \dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
We can write this expression as,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R} = \dfrac{\mu }{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
Hence we got the required expression for the concave refractive surface.
Note
According to the Cartesian sign convention,
-All distances as measured from the pole of the mirror.
-The distances that are measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive.
-The distances that are measured opposite to the direction of incident light is considered as negative.
-The height measured upward the principal axis is measured as positive and the height measured downward is measured negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




