
Describe briefly: Arithmetic growth (b) Geometric growth (c) Sigmoid growth curve (d) Absolute and relative growth rates.
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Growth rate is the speed at which the population increases due to the increase in the number of organisms. This is calculated by dividing the number of organisms at a certain interval of time by the amount of time interval.
Complete answer:
i) Arithmetic growth- It is the growth in which one daughter cell divides while all the other cells undergo differentiation and maturity accompanied by mitosis. The increase in growth occurs in the arithmetic progression at a constant rate. Example- elongation of stem at constant rate.
ii) Geometric growth- The daughter cells obtained from mitosis have the ability to divide but the rate slows down due to nutrient deficiency. In this the population size increases in multiplicative fashion. In this the growth is slow at lag phase and rapid during log phase.
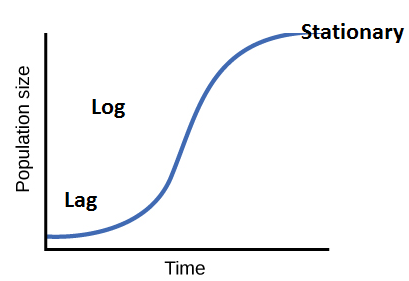
iii) Sigmoid growth curve- It is a S-shaped graph. It is obtained by plotting the growth of living organisms in their natural environment versus time. It consists of three phases- Lag phase, log phase and stationary phase. It shows rapid multiplication then equilibrium.
iv) Absolute and relative growth rate- Absolute growth rate refers to the total growth per unit time whereas relative growth rate is the growth of the given system per unit growth. Relative growth rate is the growth rate with respect to size.
Note: The exponential growth is mostly seen in bacteria. In bacteria reproduction takes place through fission. The bacteria reproduce roughly in an hour. The division and population size recorded per hour shows the exponential growth.
Complete answer:
i) Arithmetic growth- It is the growth in which one daughter cell divides while all the other cells undergo differentiation and maturity accompanied by mitosis. The increase in growth occurs in the arithmetic progression at a constant rate. Example- elongation of stem at constant rate.
ii) Geometric growth- The daughter cells obtained from mitosis have the ability to divide but the rate slows down due to nutrient deficiency. In this the population size increases in multiplicative fashion. In this the growth is slow at lag phase and rapid during log phase.
iii) Sigmoid growth curve- It is a S-shaped graph. It is obtained by plotting the growth of living organisms in their natural environment versus time. It consists of three phases- Lag phase, log phase and stationary phase. It shows rapid multiplication then equilibrium.

iv) Absolute and relative growth rate- Absolute growth rate refers to the total growth per unit time whereas relative growth rate is the growth of the given system per unit growth. Relative growth rate is the growth rate with respect to size.
Note: The exponential growth is mostly seen in bacteria. In bacteria reproduction takes place through fission. The bacteria reproduce roughly in an hour. The division and population size recorded per hour shows the exponential growth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




