
Describe the construction and working of a potentiometer. Explain the circuit diagram and how EMF of two cells can be compared with its help.
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the principle of potentiometer is described, that is the potential difference between two points is directly proportional to the length of the wire between these points. Then, discuss how it was constructed and explain how EMF of two cells can be compared by using a potentiometer.
Complete answer:
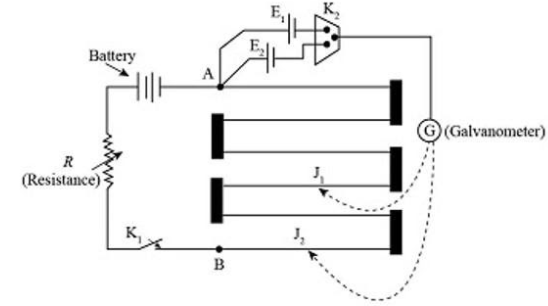
Construction of a potentiometer-
In the above diagram, $A$-Ammeter, $E$-Accumulator, ${J_1},{J_2}$-Jockey, $AB$-Potentiometer wire, $G$-Galvanometer, $Rh$ -Rheostat, ${k_1},{k_2}$ -Key.
Mainly a potentiometer is made of a uniform wire $AB$. The wire is connected from point $A$ to $B$ There is a battery whose EMF is $\left( E \right)$, connected between the wire. Once we close the keys current starts to flow through the wire and the battery maintains a uniform potential gradient along the wire. The rheostat $\left( R \right)$ is connected in series with a battery whose work is to adjust the current in the wire.
Working Principle of a potentiometer: The working principle of a potentiometer - When current flows through a wire constantly, the potential difference between any two points of the wire is directly proportional to the length of wire between these two points.
Compare EMF of two cells by using potentiometer-
In the diagram we can see there are two cells whose EMFS are ${E_1},{E_2}$.Now the positive part of the cells are connected to point $A$ and the negative part of the cells are connected to the jockey through galvanometer $\left( G \right)$. So, when the key is closed and the jockey is moved along wire $AB$ and the find the null point $\left( P \right)$ where there is no deflection in the galvanometer. Once the null point is detected, measure the length of the wire to null point $ = {l_1}$.
Now the potential difference along the length $A$ to $P$ is,
${E_1} = K{l_1}$………. (i)
[Where $K$ is the potential gradient of the wire].
Now disconnect the cell of EMF ${E_1}$ and connect the cell of EMF ${E_2}$ and repeat the procedure. Thus,
${E_2} = K{l_2}$ ……. (ii)
Now, we divide the equation (i) by equation (ii),
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}}$
As we measure the value of ${l_1},{l_2}$ we can compare the EMF of two cells.
Note: The wire must be uniform, and resistance should be higher. One thing must be kept in mind during the construction of the potentiometer that the EMF of the battery which is connected across the wire should be greater than the EMF to be compared.
Complete answer:

Construction of a potentiometer-
In the above diagram, $A$-Ammeter, $E$-Accumulator, ${J_1},{J_2}$-Jockey, $AB$-Potentiometer wire, $G$-Galvanometer, $Rh$ -Rheostat, ${k_1},{k_2}$ -Key.
Mainly a potentiometer is made of a uniform wire $AB$. The wire is connected from point $A$ to $B$ There is a battery whose EMF is $\left( E \right)$, connected between the wire. Once we close the keys current starts to flow through the wire and the battery maintains a uniform potential gradient along the wire. The rheostat $\left( R \right)$ is connected in series with a battery whose work is to adjust the current in the wire.
Working Principle of a potentiometer: The working principle of a potentiometer - When current flows through a wire constantly, the potential difference between any two points of the wire is directly proportional to the length of wire between these two points.
Compare EMF of two cells by using potentiometer-
In the diagram we can see there are two cells whose EMFS are ${E_1},{E_2}$.Now the positive part of the cells are connected to point $A$ and the negative part of the cells are connected to the jockey through galvanometer $\left( G \right)$. So, when the key is closed and the jockey is moved along wire $AB$ and the find the null point $\left( P \right)$ where there is no deflection in the galvanometer. Once the null point is detected, measure the length of the wire to null point $ = {l_1}$.
Now the potential difference along the length $A$ to $P$ is,
${E_1} = K{l_1}$………. (i)
[Where $K$ is the potential gradient of the wire].
Now disconnect the cell of EMF ${E_1}$ and connect the cell of EMF ${E_2}$ and repeat the procedure. Thus,
${E_2} = K{l_2}$ ……. (ii)
Now, we divide the equation (i) by equation (ii),
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}}$
As we measure the value of ${l_1},{l_2}$ we can compare the EMF of two cells.
Note: The wire must be uniform, and resistance should be higher. One thing must be kept in mind during the construction of the potentiometer that the EMF of the battery which is connected across the wire should be greater than the EMF to be compared.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




