
Describe the digestive system of cockroach.
Answer
523.1k+ views
Hint: The digestive system of cockroach consists of two parts i.e., alimentary canal and associated glands.
Complete Answer:
Cockroaches are omnivorous in nature and can eat all kinds of organic food sources available to them.
Parts of alimentary canal:
Alimentary canal is elongated & coiled. It starts from the mouth and ends with anus.
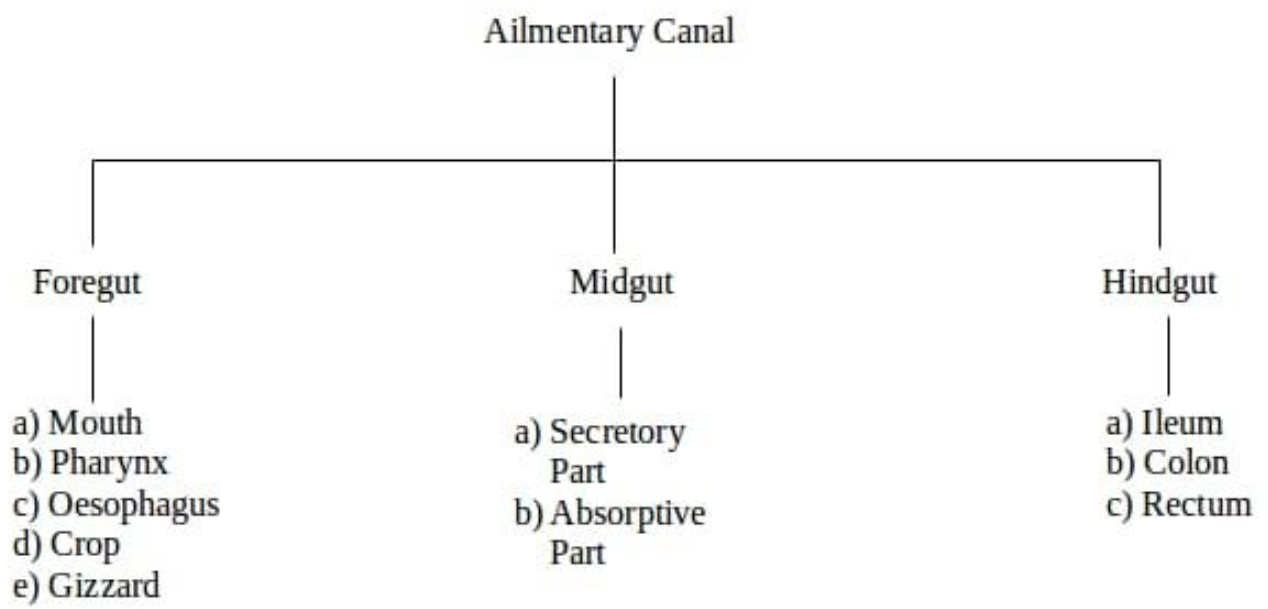
The alimentary canal of cockroach is divided into three regions: foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
1. Foregut: It consists of a mouth which is followed by a short tubular pharynx. The pharynx leads into a narrow and short tube known as oesophagus which in turn opens into a sac like structure called crop. Crop is used for storing food. The crop is followed by a gizzard. It has six teeth. Gizzard helps in grinding food particles.
2. Midgut or mesenteron: It is the middle part of the alimentary canal. Gastric or hepatic caeca (ring of 6-8 blind tubular structure) secret digestive juices that are present at the junction of foregut and midgut. Malpighian tubules (yellow color thin filamentous ring of 100-150) help in removal of excretory products present at the junction of midgut and hindgut. Mesenteron is the main site of enzyme production, digestion and absorption.
3. Hindgut: The hindgut is differentiated into: a. Ileum, b. Colon and c. Rectum. The hindgut opens outside through the anus.
Note: Digestion begins first at the mouth. The food once entering the stomach (mesenteron) is treated by the digestive enzymes secreted by the gastric caeca. Digestive glands include salivary glands, hepatic caeca and mesenteric glands.
Complete Answer:
Cockroaches are omnivorous in nature and can eat all kinds of organic food sources available to them.
Parts of alimentary canal:
Alimentary canal is elongated & coiled. It starts from the mouth and ends with anus.

The alimentary canal of cockroach is divided into three regions: foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
1. Foregut: It consists of a mouth which is followed by a short tubular pharynx. The pharynx leads into a narrow and short tube known as oesophagus which in turn opens into a sac like structure called crop. Crop is used for storing food. The crop is followed by a gizzard. It has six teeth. Gizzard helps in grinding food particles.
2. Midgut or mesenteron: It is the middle part of the alimentary canal. Gastric or hepatic caeca (ring of 6-8 blind tubular structure) secret digestive juices that are present at the junction of foregut and midgut. Malpighian tubules (yellow color thin filamentous ring of 100-150) help in removal of excretory products present at the junction of midgut and hindgut. Mesenteron is the main site of enzyme production, digestion and absorption.
3. Hindgut: The hindgut is differentiated into: a. Ileum, b. Colon and c. Rectum. The hindgut opens outside through the anus.
Note: Digestion begins first at the mouth. The food once entering the stomach (mesenteron) is treated by the digestive enzymes secreted by the gastric caeca. Digestive glands include salivary glands, hepatic caeca and mesenteric glands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




