
Describe the functions of coolant in a nuclear reactor.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The heats released by fission in nuclear reactors must be captured and transferred for use in electricity generation. To this end, reactors use coolants that remove heat from the core where the fuel is processed and carry it to electricals generators. Coolants also serve to maintain manageable pressures within the core.
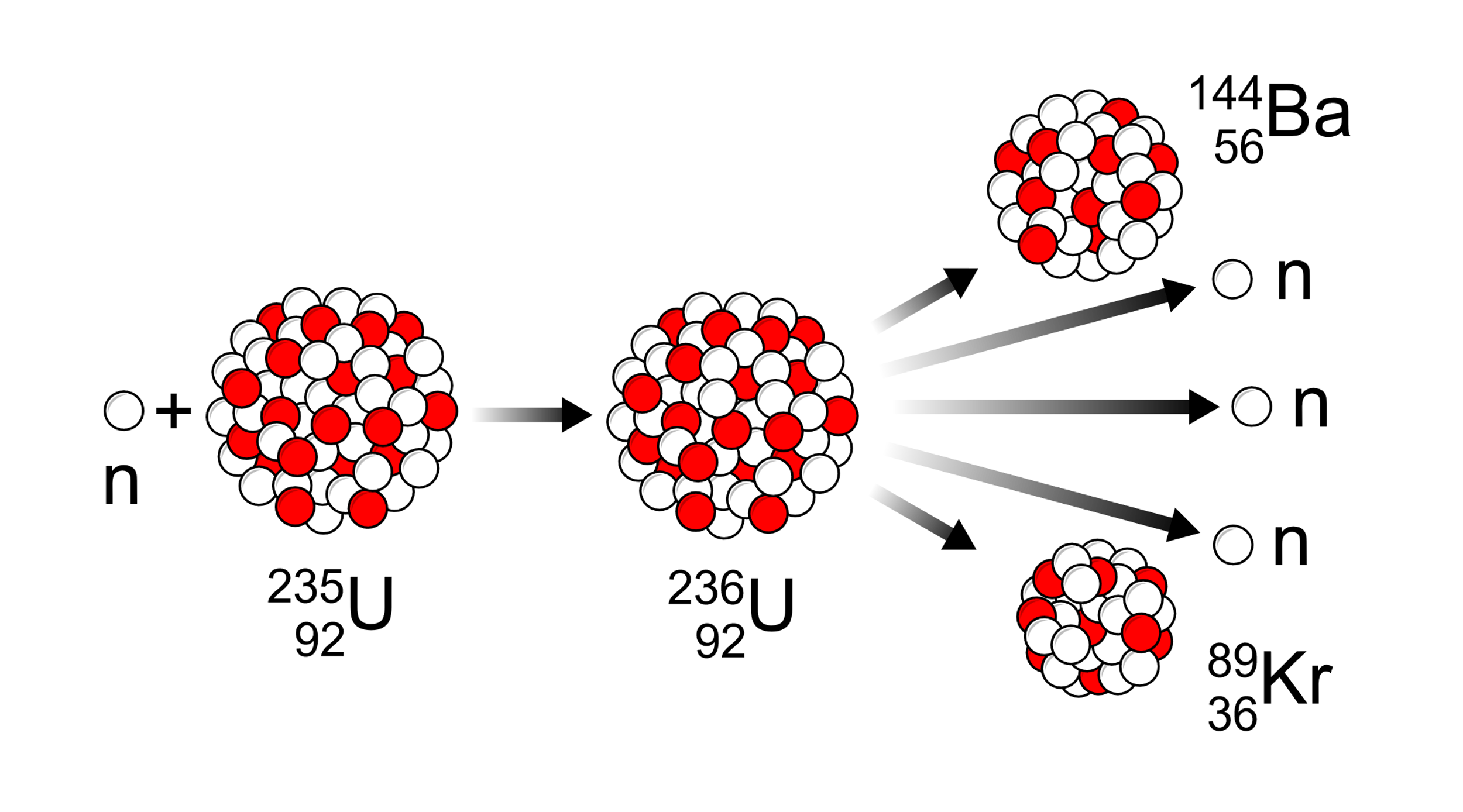
To continue the chain in a nuclear reactor we have to control the speed of neutrons released from the fission reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
The nuclear fission definition states that on a nuclear reaction the particle or an atom splits into two smaller and lighter nuclei. You must also note that when we split the atom its two daughter nuclei weigh lighter than the parent nucleus.
Liquid sodium is used as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
The high thermal conductivity properties effectively create a reservoir of heat capacity which provides thermal inertia against overheating.
Water is difficult to use as a coolant for a fast reactor because water acts as a neutron moderator that slows the fast neutrons into thermal neutrons.
The reactor uses a coolant that removes heat from the core where the fuel is processed and carries it to electrical generators. Coolants also serve to maintain manageable pressure within the core.
Heavy water, light water, sodium metal liquid is used as a coolant to observe the heat produced in a nuclear reactor and hot coolant sent to the heat exchanger to get the steam through the coolant circulation pump.
Antifreeze is used when the water-based coolant has to withstand temperatures below $0$ degrees Celsius or when its boiling point has to be raised.
Note:
Boiling water reactors/ pressurized water reactors: light water ($H_2O$)
Pressurized heavy water reactors: heavy water ($D_2O$)
Fast neutron reactors: liquid sodium ($Na_2$)
Gas-cooled reactors: carbon dioxide ($CO_2$)
These are the coolants used in respective reactors. Their usage is subject to reactor design and energy of neutrons populated in the nuclear reactors. Some other materials like ($NaK$, LEAD) can also be used as a coolant in nuclear reactors and some are under research.
To continue the chain in a nuclear reactor we have to control the speed of neutrons released from the fission reaction.

Complete step by step solution:
The nuclear fission definition states that on a nuclear reaction the particle or an atom splits into two smaller and lighter nuclei. You must also note that when we split the atom its two daughter nuclei weigh lighter than the parent nucleus.
Liquid sodium is used as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
The high thermal conductivity properties effectively create a reservoir of heat capacity which provides thermal inertia against overheating.
Water is difficult to use as a coolant for a fast reactor because water acts as a neutron moderator that slows the fast neutrons into thermal neutrons.
The reactor uses a coolant that removes heat from the core where the fuel is processed and carries it to electrical generators. Coolants also serve to maintain manageable pressure within the core.
Heavy water, light water, sodium metal liquid is used as a coolant to observe the heat produced in a nuclear reactor and hot coolant sent to the heat exchanger to get the steam through the coolant circulation pump.
Antifreeze is used when the water-based coolant has to withstand temperatures below $0$ degrees Celsius or when its boiling point has to be raised.
Note:
Boiling water reactors/ pressurized water reactors: light water ($H_2O$)
Pressurized heavy water reactors: heavy water ($D_2O$)
Fast neutron reactors: liquid sodium ($Na_2$)
Gas-cooled reactors: carbon dioxide ($CO_2$)
These are the coolants used in respective reactors. Their usage is subject to reactor design and energy of neutrons populated in the nuclear reactors. Some other materials like ($NaK$, LEAD) can also be used as a coolant in nuclear reactors and some are under research.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




