
Describe the human respiratory system.
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: This system involves the group of organs and tissues that helps in breathing and gaseous exchange. The process of gaseous exchange occurs in the lungs. They are the primary organs that are located in the thorax.
Complete answer:
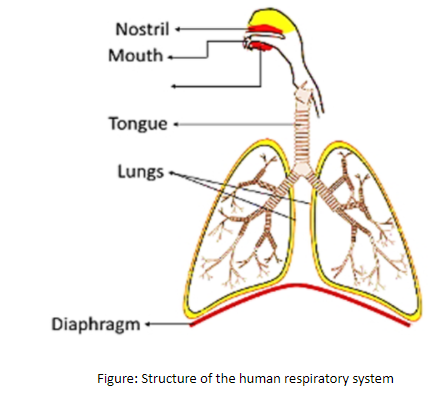
In the human respiratory system, the cells utilize oxygen for metabolism and produce energy along with carbon dioxide which is harmful. The human respiratory system involves different parts for the exchange of gases:
External nostrils: They are present in a pair that opens out above the upper lips. They help in the intake of air.
Nasal chamber: External nostrils lead to a nasal chamber which is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air and remove dust.
Nasopharynx: It is a passage behind the nasal chamber which is common for food and air.
Larynx: It is a cartilaginous box which is also called a sound box. It helps in sound production.
Trachea: The trachea is a tube that extends up to the mid-thoracic cavity. It forms bronchi by dividing at the level of the 5th thoracic vertebra.
Bronchi: The trachea divides the 5th thoracic vertebra into left and right bronchi.
Bronchioles: Each bronchus further divided to form the secondary and tertiary bronchi and bronchioles.
Alveoli: Each terminal bronchiole forms several very thin, irregular walled and vascularized bag-like structures called alveoli.
Lungs: The lungs involve the branching network of bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. They are present in a pair which are covered by a double-layered pleura. There is a pleural fluid-filled between the lungs and pleura.
Diaphragm: It is the strong wall of muscle that creates the suction to draw in air and expands the lungs.
Note: -The pleural fluid helps in the reduction of friction on the lung-surface.
-The diaphragm and the external and internal intercostals muscles between the ribs help in breathing.
-Oxygen binds with hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin and each hemoglobin molecule can carry a maximum of four molecules of oxygen.
Complete answer:
In the human respiratory system, the cells utilize oxygen for metabolism and produce energy along with carbon dioxide which is harmful. The human respiratory system involves different parts for the exchange of gases:
External nostrils: They are present in a pair that opens out above the upper lips. They help in the intake of air.
Nasal chamber: External nostrils lead to a nasal chamber which is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air and remove dust.
Nasopharynx: It is a passage behind the nasal chamber which is common for food and air.
Larynx: It is a cartilaginous box which is also called a sound box. It helps in sound production.
Trachea: The trachea is a tube that extends up to the mid-thoracic cavity. It forms bronchi by dividing at the level of the 5th thoracic vertebra.
Bronchi: The trachea divides the 5th thoracic vertebra into left and right bronchi.
Bronchioles: Each bronchus further divided to form the secondary and tertiary bronchi and bronchioles.
Alveoli: Each terminal bronchiole forms several very thin, irregular walled and vascularized bag-like structures called alveoli.
Lungs: The lungs involve the branching network of bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. They are present in a pair which are covered by a double-layered pleura. There is a pleural fluid-filled between the lungs and pleura.
Diaphragm: It is the strong wall of muscle that creates the suction to draw in air and expands the lungs.

Note: -The pleural fluid helps in the reduction of friction on the lung-surface.
-The diaphragm and the external and internal intercostals muscles between the ribs help in breathing.
-Oxygen binds with hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin and each hemoglobin molecule can carry a maximum of four molecules of oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




