
Describe the initiation process of transcription in bacteria.
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Transcription is a vital process that takes place in the cells to make a transcript that is used to make proteins. To make the transcript the DNA needs to get unwind. As the transcription enzymes need to read it by binding to the template strand. This is followed by the elongation and termination steps of transcription.
Complete step by step answer: Transcription refers to the process of formation of the mRNA from the DNA. It can also be termed as the transcript. This process involves complementary base pairing that is catalyzed by an RNA polymerase enzyme. The transcript is produced in a unidirectional manner $5'to3'$.
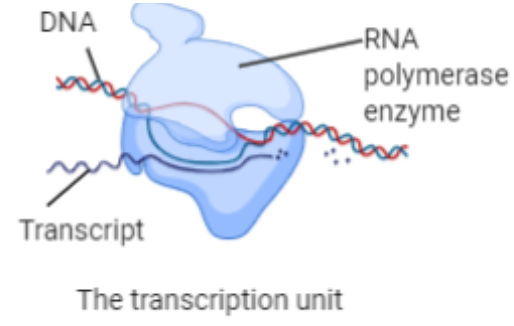
The initiation process is the first step in transcription. As bacteria are prokaryotic organisms the process is simple. The initiation begins with the RNA polymerase enzyme. The $\sigma $ (sigma) factor of RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter sequence in the double helix DNA. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence that covers around $80bp$ from $-55$ to $+20$ position of DNA sequence. This results in the formation of a binary complex because the DNA is in the duplex form that will be converted into an open complex (unwind form) by melting a short region of DNA that is an A-T rich region within the promoter sequence. The structure so formed is called the transcription bubble. Now, for the melting of the A-T rich region, the RNA polymerase needs some transcription factors that are A, B, D, E, F, and H and transcription factors II H-TF II H. TF II H forms the transcription bubble. Some dNTPs are also required that are Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine. After the association of all these factors with the enzyme, the complex of DNA, RNA, and enzyme is called the ternary complex. Transcription is not usually successful in two or three attempts. It gets terminated until and unless the transcript becomes of length $10bp$.
Note: The DNA-RNA hybrid formed in initiation is important for the elongation of the transcript. The dNTPs are added to form the transcript by covalent phosphodiester bonds using DNA-RNA hybrid.
Complete step by step answer: Transcription refers to the process of formation of the mRNA from the DNA. It can also be termed as the transcript. This process involves complementary base pairing that is catalyzed by an RNA polymerase enzyme. The transcript is produced in a unidirectional manner $5'to3'$.

The initiation process is the first step in transcription. As bacteria are prokaryotic organisms the process is simple. The initiation begins with the RNA polymerase enzyme. The $\sigma $ (sigma) factor of RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter sequence in the double helix DNA. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence that covers around $80bp$ from $-55$ to $+20$ position of DNA sequence. This results in the formation of a binary complex because the DNA is in the duplex form that will be converted into an open complex (unwind form) by melting a short region of DNA that is an A-T rich region within the promoter sequence. The structure so formed is called the transcription bubble. Now, for the melting of the A-T rich region, the RNA polymerase needs some transcription factors that are A, B, D, E, F, and H and transcription factors II H-TF II H. TF II H forms the transcription bubble. Some dNTPs are also required that are Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine. After the association of all these factors with the enzyme, the complex of DNA, RNA, and enzyme is called the ternary complex. Transcription is not usually successful in two or three attempts. It gets terminated until and unless the transcript becomes of length $10bp$.
Note: The DNA-RNA hybrid formed in initiation is important for the elongation of the transcript. The dNTPs are added to form the transcript by covalent phosphodiester bonds using DNA-RNA hybrid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




