
Describe the oxy-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: This curve plots the proportion of hemoglobin in its saturated form on the vertical axis against the oxygen tension on the horizontal axis and is of sigmoid shape.
Complete answer:
The transport of the oxygen from the lungs to the target tissues of the body by the blood is due to the ability of hemoglobin to combine reversibly by the oxygen.
At a tension of 100 mm Hg or more than this, the hemoglobin is completely saturated. The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen in the blood.
The vital relationship between the saturation of hemoglobin and the oxygen tension is shown by the dissociation curve in which percent saturation is plotted with the oxygen tension. The curve is drawn with carbonic oxide at a tension of 40 mm of Hg, this is considered as representative of normal physiological condition.
The hemoglobin in this condition is 94 – 98% saturated in the arterial blood. This saturation of hemoglobin declines slowly with the fall in oxygen tension and rapid unloading of oxygen takes place at the oxygen tension of 50 mm Hg. This is the unloading tension of hemoglobin.
While in tissues the oxygen tension is about 40 mm of Hg which helps in the dissociation of the oxy-hemoglobin complex making the oxygen readily available to the cells.
Additional Information:
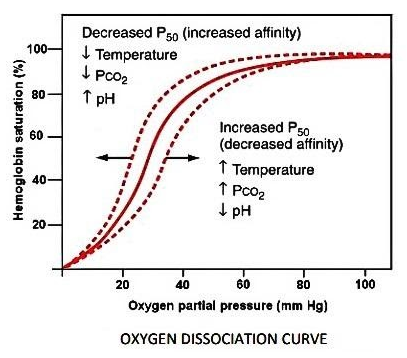
Factors affecting Dissociation of Oxy-haemoglobin-
-temperature
- The rise in temperature leads to a decrease in the hemoglobin saturation.
-Effect of carbon dioxide
-The influence of carbon dioxide on the shape of the dissociation curve is the effect of the formation of carbonic acid.
-The carbonic acid makes the pH go lower and creates an acidity which facilitates the dissociation of oxy-hemoglobin.
-This ability of carbon dioxide to shift the curve to the right is called a Bohr effect.
Note:
When hemoglobin combines with carbon monoxide the complex carboxyhemoglobin is formed. Which in turn reduces the amount of hemoglobin to carry oxygen.
When the decrease in the normal oxygen concentration happens then it results in the formation of bluish skin which is called cyanosis.
Complete answer:
The transport of the oxygen from the lungs to the target tissues of the body by the blood is due to the ability of hemoglobin to combine reversibly by the oxygen.
At a tension of 100 mm Hg or more than this, the hemoglobin is completely saturated. The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen in the blood.
The vital relationship between the saturation of hemoglobin and the oxygen tension is shown by the dissociation curve in which percent saturation is plotted with the oxygen tension. The curve is drawn with carbonic oxide at a tension of 40 mm of Hg, this is considered as representative of normal physiological condition.
The hemoglobin in this condition is 94 – 98% saturated in the arterial blood. This saturation of hemoglobin declines slowly with the fall in oxygen tension and rapid unloading of oxygen takes place at the oxygen tension of 50 mm Hg. This is the unloading tension of hemoglobin.
While in tissues the oxygen tension is about 40 mm of Hg which helps in the dissociation of the oxy-hemoglobin complex making the oxygen readily available to the cells.

Additional Information:
Factors affecting Dissociation of Oxy-haemoglobin-
-temperature
- The rise in temperature leads to a decrease in the hemoglobin saturation.
-Effect of carbon dioxide
-The influence of carbon dioxide on the shape of the dissociation curve is the effect of the formation of carbonic acid.
-The carbonic acid makes the pH go lower and creates an acidity which facilitates the dissociation of oxy-hemoglobin.
-This ability of carbon dioxide to shift the curve to the right is called a Bohr effect.
Note:
When hemoglobin combines with carbon monoxide the complex carboxyhemoglobin is formed. Which in turn reduces the amount of hemoglobin to carry oxygen.
When the decrease in the normal oxygen concentration happens then it results in the formation of bluish skin which is called cyanosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




