
Describe the process of transcription in prokaryotes/bacteria.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The process of the formation of RNA from DNA with the help of various enzymes.
Complete answer:
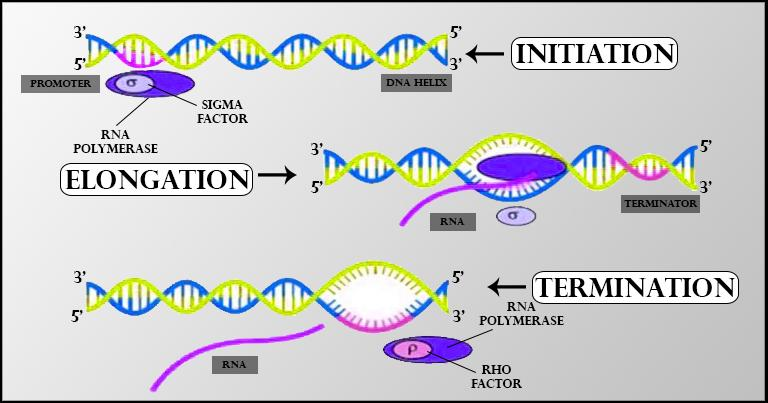
Prokaryotic transcription also known as bacterial transcription is the process in which a segment of bacterial DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) which is later translated to produce proteins with the use of the enzyme RNA polymerase and other transcription factors.
Both bacterial transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm of the cell. The process occurs in three main steps:
Initiation – In this step, the double helix DNA strand is unwounded and becomes single-stranded near the initiation site. The RNA polymerase enzyme binds to the promoter sequence (Pribnow box / TATA box) and starts the transcription of the single-stranded DNA. The sigma factors are responsible for the binding of the RNA polymerase enzyme to the promoter.
Elongation – After the synthesis of more than 10 base pairs of long RNA, the sigma factor is removed from the promoter. The RNA polymerase enzyme then moves in 5’ – 3’ direction continuously all the while synthesizing RNA.
Termination – This is the last stage that stops the process of transcription. It has two types of mechanisms-
-Rho-independent transcription termination – transcription is terminated due to a specific sequence in terminator DNA. The terminator DNA contains invert repeats which cause complementary pairing as transcript RNA from the hairpin structure. This results in the dissociation of RNA polymerase from the DNA template.
-Rho-dependent transcription termination – transcription is terminated by rho protein. It binds to RNA after the translation has completed but transcription is still going on. This factor causes dissociation of RNA polymerase from the DNA.
Note: Bacterial transcription differs from eukaryotic transcription, as in bacteria transcription and translation both can occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm of the cell whereas in eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Bacterial RNA polymerase is only of one type whereas eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerase enzymes.
Complete answer:
Prokaryotic transcription also known as bacterial transcription is the process in which a segment of bacterial DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) which is later translated to produce proteins with the use of the enzyme RNA polymerase and other transcription factors.
Both bacterial transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm of the cell. The process occurs in three main steps:
Initiation – In this step, the double helix DNA strand is unwounded and becomes single-stranded near the initiation site. The RNA polymerase enzyme binds to the promoter sequence (Pribnow box / TATA box) and starts the transcription of the single-stranded DNA. The sigma factors are responsible for the binding of the RNA polymerase enzyme to the promoter.
Elongation – After the synthesis of more than 10 base pairs of long RNA, the sigma factor is removed from the promoter. The RNA polymerase enzyme then moves in 5’ – 3’ direction continuously all the while synthesizing RNA.
Termination – This is the last stage that stops the process of transcription. It has two types of mechanisms-
-Rho-independent transcription termination – transcription is terminated due to a specific sequence in terminator DNA. The terminator DNA contains invert repeats which cause complementary pairing as transcript RNA from the hairpin structure. This results in the dissociation of RNA polymerase from the DNA template.
-Rho-dependent transcription termination – transcription is terminated by rho protein. It binds to RNA after the translation has completed but transcription is still going on. This factor causes dissociation of RNA polymerase from the DNA.

Note: Bacterial transcription differs from eukaryotic transcription, as in bacteria transcription and translation both can occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm of the cell whereas in eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Bacterial RNA polymerase is only of one type whereas eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerase enzymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




