
Describe the stages in the life cycle of silkworm.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint:Silk is obtained from silkworms. The silkworm grows from an egg to successive larval and pupal stage, and finally into an adult moth. Cocoons spun by different types of moths yield different types of silk.
Complete answer:
The silk fibres come from the silk moth cocoons. The life cycle of the silkworm consists of four stages. The first stage of the life cycle of a silkworm is the egg. The female moth lays eggs that hatch into the larvae called caterpillars or silkworms. They grow in size, and when the caterpillar is ready to reach the next stage of its life cycle called pupa, it first weaves a web to hang on to itself and moves its head from side to side. During these movements of the head, the caterpillar secretes fibre made from a protein that hardens when exposed to air and becomes a silk fibre. Soon the caterpillar fully covers themselves with silk fibres. This cover is known as a cocoon.
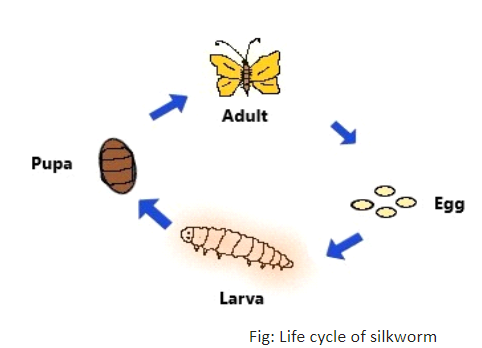
After the final molt within the cocoon, the larva transforms into a brown, chitin-covered form called the pupa. Within the cocoon, the further growth of the moth continues. The silk yarn (thread) is made from the cocoon of the silk moth.
Note:The colour of the silk filament can be determined by the diet of the larvae and seasonal effects. Mulberry leaves produce the desired lighter coloured cocoons, although other plants also produce a range of colours in wild silkworms.
Complete answer:
The silk fibres come from the silk moth cocoons. The life cycle of the silkworm consists of four stages. The first stage of the life cycle of a silkworm is the egg. The female moth lays eggs that hatch into the larvae called caterpillars or silkworms. They grow in size, and when the caterpillar is ready to reach the next stage of its life cycle called pupa, it first weaves a web to hang on to itself and moves its head from side to side. During these movements of the head, the caterpillar secretes fibre made from a protein that hardens when exposed to air and becomes a silk fibre. Soon the caterpillar fully covers themselves with silk fibres. This cover is known as a cocoon.

After the final molt within the cocoon, the larva transforms into a brown, chitin-covered form called the pupa. Within the cocoon, the further growth of the moth continues. The silk yarn (thread) is made from the cocoon of the silk moth.
Note:The colour of the silk filament can be determined by the diet of the larvae and seasonal effects. Mulberry leaves produce the desired lighter coloured cocoons, although other plants also produce a range of colours in wild silkworms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




