
Describe the structure of a monocot seed.
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint: A monocotyledonous seed has a single cotyledon in it with a thick seed coat and it gets fused with the pericarp. These seeds are endospermic in nature. The cotyledons in the monocot seed are known as scutellum and are supplied with the shoot axis.
Complete answer:
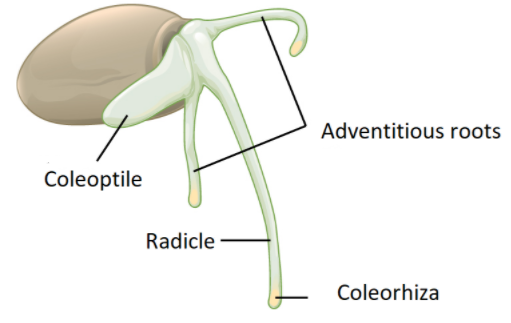
The monocot seed has the outer seed coat and the inner seed coat. Within these layers the embryo is known to occur. This monocot seed is differentiated due to the separate axis. The part of the axis that is present in the decrease phase of the seed is referred to as radical. This part blanketed through the sheath is referred to as coleoptile. The part of the axis that is present in the higher part of the stem is called plumule.
The plumule is covered by a sheath called coleoptile. After the germination of the seed, the water enters into the gap of mycorrhiza and the seed bulges.
This motivates the boom of the seed, in which the stem section of the seed grows from the elongation of the plumule by destroying the layer of coleoptile and the root types from the radicle through the breaking of the coleorhiza. The endosperm is present and located in the internal phase of the seed around the embryo. This is the nutritive layer that provides nutrition for the increase of the embryo; the monocot seed possesses the aleurone layer which is the layer of protein that is existing in between the endosperm and the outer covering of the seed.
Note: The example for the monocot seeds includes the grains like rice, wheat, maize, barley etc., onion, banana, palm, ginger, coconut, garlic, bamboo, Lillie, tulips etc. All of these flora possess solely one cotyledon or the scutellum in the seed of these plants. The dicotyledonous plants possess two cotyledons. For example-Mango.
Complete answer:
The monocot seed has the outer seed coat and the inner seed coat. Within these layers the embryo is known to occur. This monocot seed is differentiated due to the separate axis. The part of the axis that is present in the decrease phase of the seed is referred to as radical. This part blanketed through the sheath is referred to as coleoptile. The part of the axis that is present in the higher part of the stem is called plumule.
The plumule is covered by a sheath called coleoptile. After the germination of the seed, the water enters into the gap of mycorrhiza and the seed bulges.
This motivates the boom of the seed, in which the stem section of the seed grows from the elongation of the plumule by destroying the layer of coleoptile and the root types from the radicle through the breaking of the coleorhiza. The endosperm is present and located in the internal phase of the seed around the embryo. This is the nutritive layer that provides nutrition for the increase of the embryo; the monocot seed possesses the aleurone layer which is the layer of protein that is existing in between the endosperm and the outer covering of the seed.

Note: The example for the monocot seeds includes the grains like rice, wheat, maize, barley etc., onion, banana, palm, ginger, coconut, garlic, bamboo, Lillie, tulips etc. All of these flora possess solely one cotyledon or the scutellum in the seed of these plants. The dicotyledonous plants possess two cotyledons. For example-Mango.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




