
Describe the structure of HIV with a diagram.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus having an incubation period of 10 years and it attacks the immune system of humans. It is of the shape of a ball.
Correct step by step answer:
HIV eventually spread to humans over the years but originated in non- human primates. This disease was clinically diagnosed in the year 1980s even though it was around for a long time. Ever since 1980, it has spread all over the world and killed over 25 million people since now.
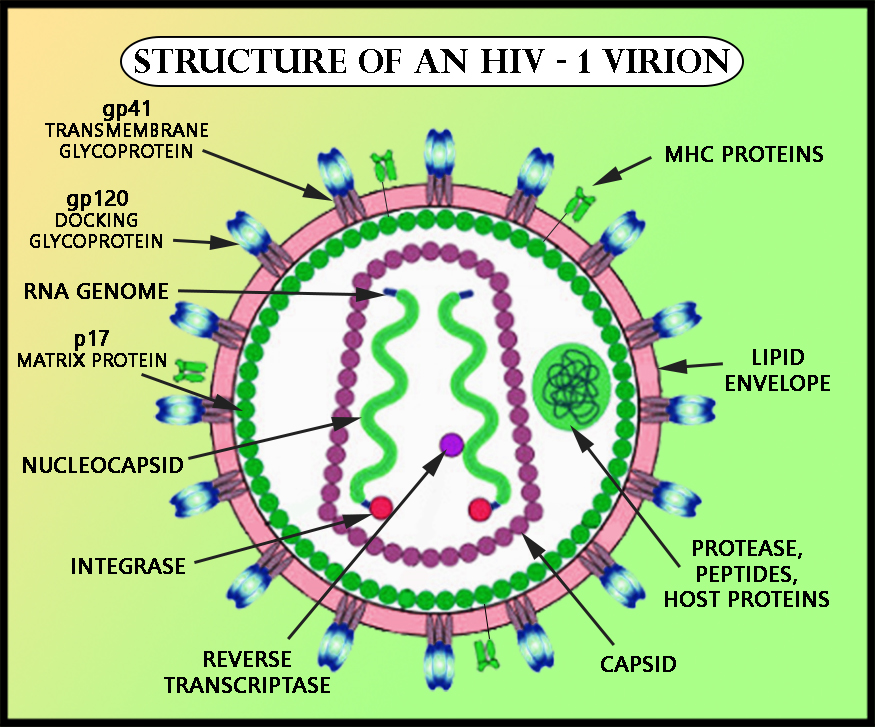
HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus that is spherical or oval in shape. The virus consists of a capsid nucleus containing the genetic material enclosed by a protein envelope. Many glycoprotein spikes are present over the protein envelope. The outer portion of a glycoprotein (gp) gp120 is connected to the inner component gp41. The HIV envelope also contains some other proteins such as Human Leukocyte Antigen(HLA). The HIV genome consists of a folded form of two helices RNA molecules. The reverse transcriptase enzymes are also present which are responsible for the conversion of the RNA into DNA. One more enzyme called integrase is also present which has got a very important role in introducing the viral genome into the host cell.
The incubation period of the HIV virus is very long i.e., almost 10 years before it starts to attack the immune system. Since the immune system is the human body’s natural defense mechanism, and after an HIV attack it becomes very weak as a result it seems harder for the patient to fight off infections and diseases.
Note:
- HIV demolishes a particular type of WBC (White Blood Cells) and the T-helper cells also known as CD4 cells by making copies of itself inside these cells.
- In HIV two very important enzymes are present: reverse transcriptase enzyme and integrase enzyme.
Correct step by step answer:
HIV eventually spread to humans over the years but originated in non- human primates. This disease was clinically diagnosed in the year 1980s even though it was around for a long time. Ever since 1980, it has spread all over the world and killed over 25 million people since now.

HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus that is spherical or oval in shape. The virus consists of a capsid nucleus containing the genetic material enclosed by a protein envelope. Many glycoprotein spikes are present over the protein envelope. The outer portion of a glycoprotein (gp) gp120 is connected to the inner component gp41. The HIV envelope also contains some other proteins such as Human Leukocyte Antigen(HLA). The HIV genome consists of a folded form of two helices RNA molecules. The reverse transcriptase enzymes are also present which are responsible for the conversion of the RNA into DNA. One more enzyme called integrase is also present which has got a very important role in introducing the viral genome into the host cell.
The incubation period of the HIV virus is very long i.e., almost 10 years before it starts to attack the immune system. Since the immune system is the human body’s natural defense mechanism, and after an HIV attack it becomes very weak as a result it seems harder for the patient to fight off infections and diseases.
Note:
- HIV demolishes a particular type of WBC (White Blood Cells) and the T-helper cells also known as CD4 cells by making copies of itself inside these cells.
- In HIV two very important enzymes are present: reverse transcriptase enzyme and integrase enzyme.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




