
Describe Watson and Crick model of DNA.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: A double-stranded, antiparallel, right-handed helix is the structure of DNA, as represented in the model of Watson and Crick. The DNA strands' sugar-phosphate backbones make up the outside of the helix. On the inside, the nitrogenous bases are established and form hydrogen-bonded pairs that keep together the DNA strands.
Complete answer:
• DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule containing the instructions required to grow, live and reproduce an organism.
• It is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four main types of macromolecules considered to be important to all life forms.
• DNA's three-dimensional structure, first suggested in \[1953\] by James D. Watson and Francis H. C. Crick, consists of two long helical strands that are coiled to form a double helix around a central axis.
• Two polymer strands coiled around each other are used in each DNA molecule.
• Each strand has a \[5'\]end (with a group of phosphate) and a \[3'\] end (with a hydroxyl group).
• The strands are antiparallel, meaning one strand runs in a direction from \[5'\] to \[3'\] , while the other strand runs in a direction from \[3'\] to \[5'\] .
• The diameter of the double helix is $2nm$ , and at an interval of $3.4nm$ , the double helical structure repeats, corresponding to ten base pairs.
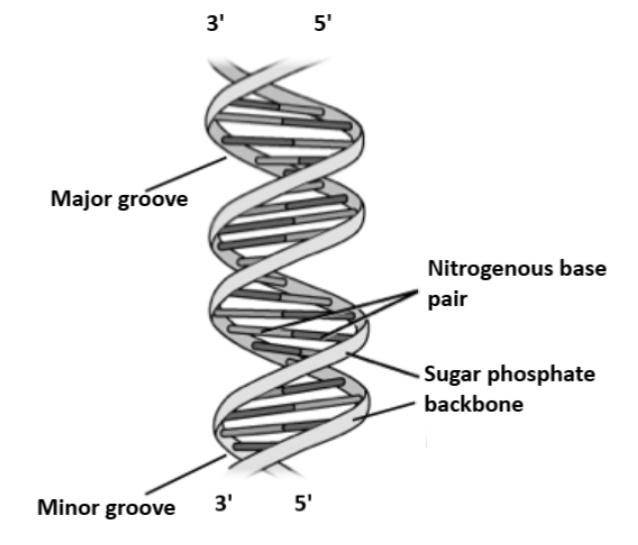
Note: If an A on one strand is detected, it must be combined with a T on the other (and vice versa). Similarly, for a partner on the opposite strand, a G located on one strand must always have a C. These associations of A-T and G-C are known as complementary base pairs. Since a large purine (A or G) is often combined with a small pyrimidine (T or C), the helix's diameter is uniform, reaching approximately \[222\] nanometers.
Complete answer:
• DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule containing the instructions required to grow, live and reproduce an organism.
• It is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four main types of macromolecules considered to be important to all life forms.
• DNA's three-dimensional structure, first suggested in \[1953\] by James D. Watson and Francis H. C. Crick, consists of two long helical strands that are coiled to form a double helix around a central axis.
• Two polymer strands coiled around each other are used in each DNA molecule.
• Each strand has a \[5'\]end (with a group of phosphate) and a \[3'\] end (with a hydroxyl group).
• The strands are antiparallel, meaning one strand runs in a direction from \[5'\] to \[3'\] , while the other strand runs in a direction from \[3'\] to \[5'\] .
• The diameter of the double helix is $2nm$ , and at an interval of $3.4nm$ , the double helical structure repeats, corresponding to ten base pairs.

Note: If an A on one strand is detected, it must be combined with a T on the other (and vice versa). Similarly, for a partner on the opposite strand, a G located on one strand must always have a C. These associations of A-T and G-C are known as complementary base pairs. Since a large purine (A or G) is often combined with a small pyrimidine (T or C), the helix's diameter is uniform, reaching approximately \[222\] nanometers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




