
Describe with the help of a suitable diagram how one can demonstrate that EMF can be induced in a coil due to change of magnetic flux and state Faraday Law of electromagnetic induction.
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint:Electromagnetic induction, also known as induction, is a mechanism in which a conductor is placed in a certain location and the magnetic field varies or remains stationary while the conductor moves. A voltage or EMF (Electromotive Force) is generated through the electrical conductor as a result of this.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is known as the generation of an emf in a conductor by varying the magnetic flux associated with it.
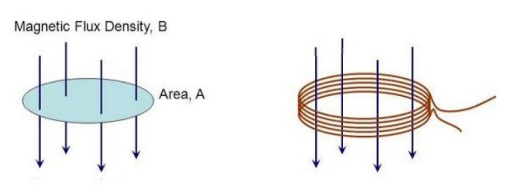
Assume that two spherical coils are positioned in close proximity to one another. As the current in one coil varies, the magnetic field generated by the current changes as well. When another coil is exposed to a shifting magnetic field, it causes a current to flow in the opposite direction. If we bind a galvanometer to a coil and send a current through it. The pointer of the galvanometer attached to the second coil indicates deflection as soon as current is applied to the coil. Current can be induced in a coil in two ways. Either shift the magnetic field across it or place it in the magnetic field. Moving a coil inside a magnetic field is a convenient way to cause current.
Faraday's First law: When a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field, an EMF (called induced emf) is induced through the conductor, and if the conductor is a closed circuit, induced current passes across it.The magnetic field can be changed in a number of ways:
-By rotating a magnet.
-The coil is moved.
-Revolving the coil with respect to the magnetic field.
Second Law of Faraday: The magnitude of induced emf is proportional to the rate of shift of flux linkages with the coil, according to Faraday's second law of electromagnetic induction. The number of turns multiplied by the flux connected with the coil equals the flux linkages.
Note:The electromagnetic work that would be done on an electric charge (an electron in this case) if it travelled once around a closed loop of conductor is defined as emf in electromagnetic induction. The electric potential's scalar field is not specified for a time-varying magnetic flux connecting a loop due to a circulating electric vector field, but an emf does function and can be calculated as a simulated electric potential across the loop.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is known as the generation of an emf in a conductor by varying the magnetic flux associated with it.

Assume that two spherical coils are positioned in close proximity to one another. As the current in one coil varies, the magnetic field generated by the current changes as well. When another coil is exposed to a shifting magnetic field, it causes a current to flow in the opposite direction. If we bind a galvanometer to a coil and send a current through it. The pointer of the galvanometer attached to the second coil indicates deflection as soon as current is applied to the coil. Current can be induced in a coil in two ways. Either shift the magnetic field across it or place it in the magnetic field. Moving a coil inside a magnetic field is a convenient way to cause current.
Faraday's First law: When a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field, an EMF (called induced emf) is induced through the conductor, and if the conductor is a closed circuit, induced current passes across it.The magnetic field can be changed in a number of ways:
-By rotating a magnet.
-The coil is moved.
-Revolving the coil with respect to the magnetic field.
Second Law of Faraday: The magnitude of induced emf is proportional to the rate of shift of flux linkages with the coil, according to Faraday's second law of electromagnetic induction. The number of turns multiplied by the flux connected with the coil equals the flux linkages.
Note:The electromagnetic work that would be done on an electric charge (an electron in this case) if it travelled once around a closed loop of conductor is defined as emf in electromagnetic induction. The electric potential's scalar field is not specified for a time-varying magnetic flux connecting a loop due to a circulating electric vector field, but an emf does function and can be calculated as a simulated electric potential across the loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




